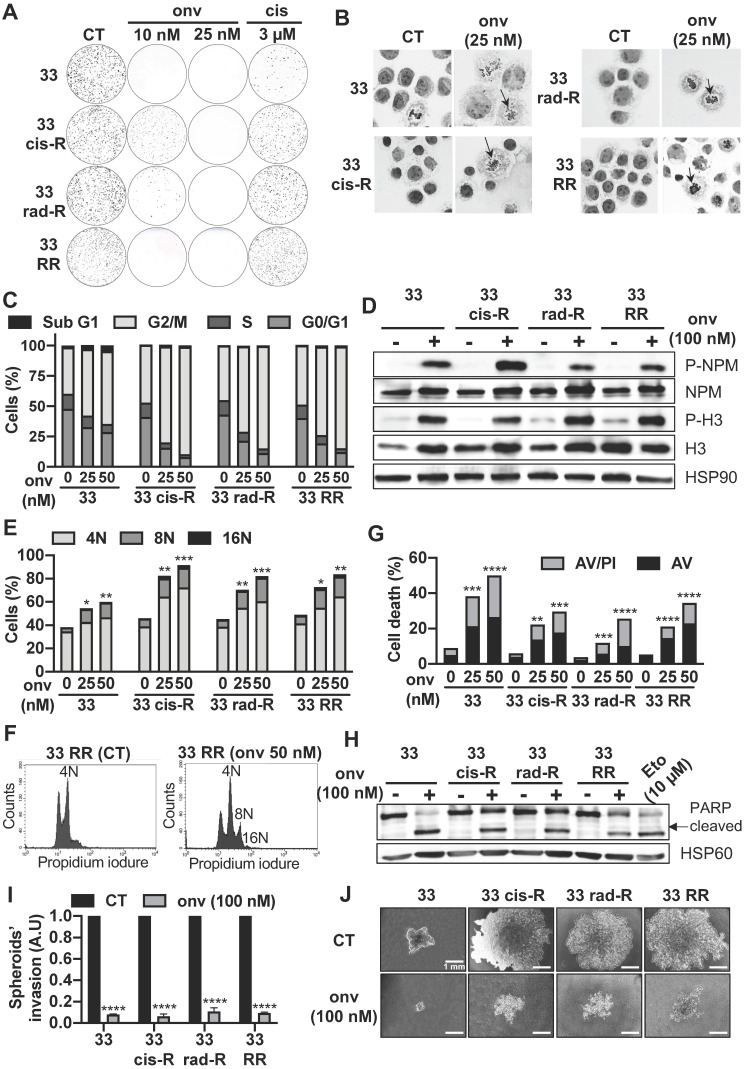
Figure 3.
Onvansertib effects on sensitive and resistant CAL33 cell lines. (A) Clonogenicity assay of sensitive and resistant CAL33 cell lines after onvansertib (10 nM and 25 nM) or cisplatin (3 μM) treatment (n = 2). (B) Hematoxylin eosin saffron staining of sensitive and resistant CAL33 cell lines treated with onvansertib (25 nM) for 24 h. Abnormal mitosis was indicated with an arrow. (C-D) Cells were treated with onvansertib (25 nM, 50 nM or 100 nM) for 24 h. Cell cycle was measured by flow cytometry (n = 3) (C), G2/M arrest was evaluated by phospho-NPM and, phospho-H3 immunoblotting. HSP90 served as a loading control (n = 2) (D). (E-F) Polyploidy (number of nuclei 8N and 16N) was assessed by flow cytometry (n = 3) (E). Representation of polyploidy in CAL33 RR (F). (G) Cells were treated with onvansertib (25 nM and 50 nM) for 48 h. Cell death was evaluated by flow cytometry. Cells were stained with propidium iodure (PI) and Annexin V (AV). Histograms show AV+/PI- cells (early apoptosis) and AV+/PI+ cells (late-apoptosis or another cell death) (n = 3). (H) Immunostaining of PARP expression on CAL33 cell lines after exposure to onvansertib (100 nM) for 24 h. HSP60 served as loading control (n = 2). (I-J) Invasion of sensitive and resistant CAL33 cells using 3D cell culture assay (spheroids) after 6 days of onvansertib treatment (100 nM) grown in (I). Results are represented as arbitrary units (the no-treatment condition was used as a control) (n = 2) (J). Statistics were analyzed using ANOVA tests: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.