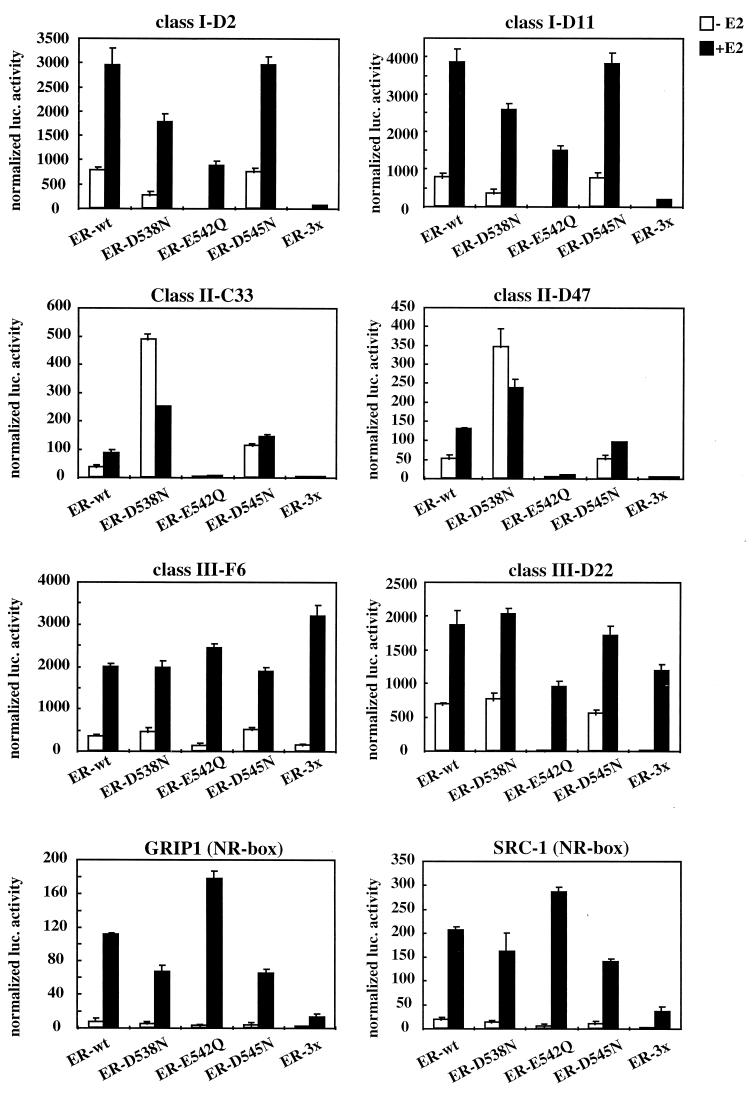
FIG. 4.
The interaction of ERα with each of the three classes of LXXLL peptides identified is affected differentially by helix 12 mutations. The contributions of each of the three charged residues (D538, E542, D545) within helix 12 to LXXLL motif-ERα interactions were evaluated. Specifically, we created single point mutations of each residue to their corresponding amides and evaluated the impact of these mutations on ERα-LXXLL peptide interactions in a mammalian two-hybrid assay. The mutants indicated were generated by site-directed mutagenesis within the wild-type (wt) VP16-ERα backbone. Selected peptide sequences representing each of the three LXXLL classes were expressed as Gal4DBD fusions. The binding capacity of the different peptides to wild-type and mutant ER was measured by using a 5×Gal4Luc3 reporter construct. GRIP-1 (NR-box) and SRC-1 (NR-box) constructs contain the center three copies of an LXXLL motif (amino acids 629 to 760 for GRIP-1 and 621 to 765 for SRC-1) fused to Gal4DBD.