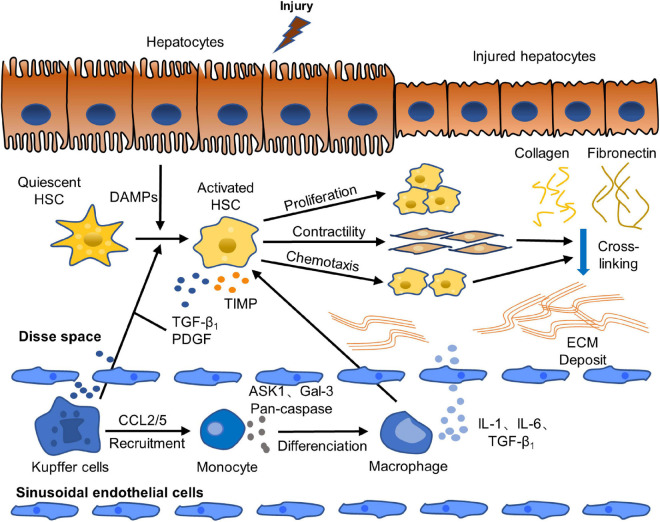
FIGURE 1.
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Activation of HSCs is a crucial step of the occurrence and progression of liver fibrosis. Quiescent HSCs are activated to fibrogenic phenotype by DAMPs released by injured hepatocytes. Activated HSCs are continuously activated and proliferated by paracrine and autocrine. They secret abundant fibrogenic cytokines and produce excessive ECM, which causes the break of the balance of pro-fibrosis/anti-fibrosis mechanism. The pro-fibrosis mechanism leads to the abnormal formation of scar and eventually induces liver fibrosis (Tacke and Weiskirchen, 2012; Roehlen et al., 2020).