FIGURE 2.
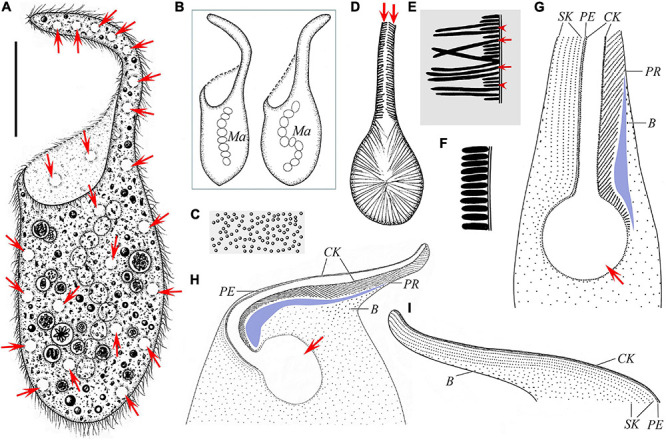
Schematic drawings of Paradileptus elephantinus from life (A–F) and after protargol staining (G–I). (A) Ventral view of a typical individual; arrows mark the contractile vacuoles. (B) Two individuals to show the different body shapes and distribution of macronuclear nodules. (C) Cortical granules underneath the pellicle. (D) Detail of oral apparatus, showing the oral opening, the basket supported by fibers, and the rod-shaped type II extrusomes (arrows) attached to the proboscis oral bulge. (E) Schematic drawing of a tangential optical section of the proboscis; arrows mark the elongated rod-shaped type I extrusomes; arrowheads indicate the short rod-shaped type II extrusomes. (F) Schematic drawing of a cross-section of the cortex showing the densely arranged oblong cortical granules. (G) Detail of oral region showing the circular oral opening (arrow), glabrous area (blue block), recognizable somatic kineties, perioral kinety, circumoral kinety, dorsal brush, and obliquely oriented preoral kineties. (H,I) Ciliary pattern in ventral view (H) and dorsal view (I) of anterior body portion of the same individual; arrow in panel (H) marks the oral opening. B, dorsal brush; CK, circumoral kinety; Ma, macronucleus; PE, perioral kinety; PR, preoral kineties; SK, somatic kineties. Scale bar = 70 μm (A).
