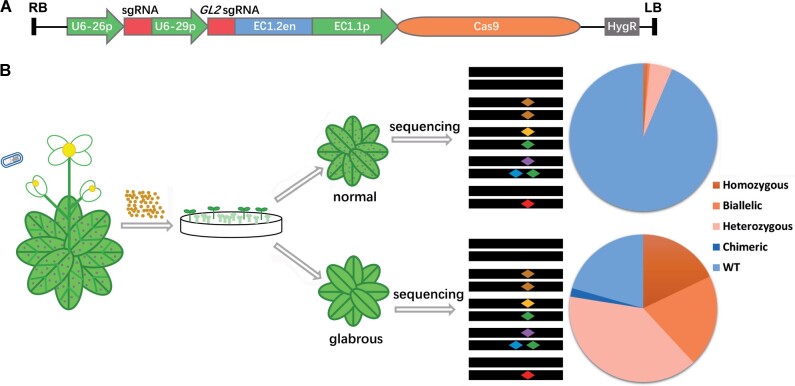
Figure 1.
Schematic showing the strategy for enrichment of homozygous and biallelic mutants in T1 plants using GBVS. A, The structure of the pEC1-GL2 plasmid. The expression of sgRNAs for GL2 and the target locus was driven by the U6-29 and U6-26 promoters, respectively. The expression of Cas9 was driven by the EC1 promoter (EC1.2 enhancer plus EC1.1 promoter). HygR, hygromycin resistance gene; RB and LB, T-DNA right and left borders, respectively. B, Outline of the GBVS strategy. pEC1-GL2 containing an sgRNA for the target locus is transformed into Col-0 plants. T1 transgenic lines are isolated on selection media and are shown as green, large seedlings. The glabrous (leaves with no trichomes, which are represented by dots) T1 plants are sequenced for indels in target gene. We assume mutations in the target gene will be enriched or reduced in glabrous and normal plants, respectively. Different colored diamonds indicate different mutations in the target site. Percentages of normal and glabrous T1 plants with WT sequences and different types of target site mutations are indicated. Portions of the images were modified from the Microsoft PowerPoint clip art database.