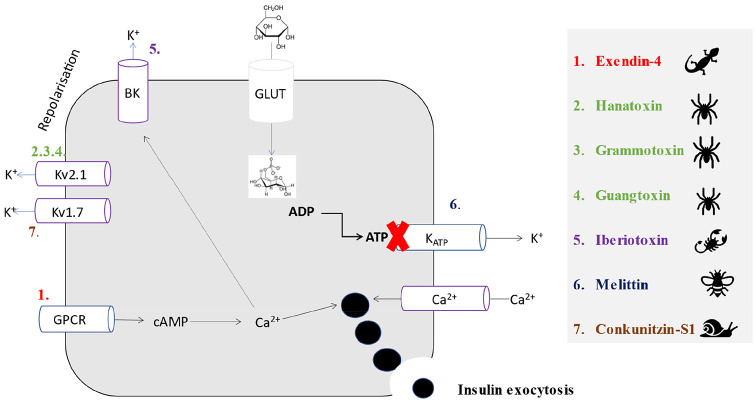
Figure 2.
A schematic showing proposed insulin secretory pathways for the venom-derived peptides hanatoxin grammotoxin, guangtoxin, exendin-4, conkunitzin-S1, iberiotoxin and melittin within pancreatic beta cells. A simplified pathway for the secretion of insulin via the primary beta cell stimulus, namely glucose, is depicted for reference via conversion to glucose-6-phospahate, with subsequent generation of ATP and closure of KATP channels. Colour coded numbers correspond to proposed beta-cell membrane target of each venom-derived peptide, with the specific K+ channel that melittin binds to still not known. Indeed, the mechanisms of all peptides, barring exendin-4, still needs to be fully characterised. Abbreviations: ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BK, calcium-activated (big) potassium channel; cAMP; cyclic adenosine monophosphate; GLUT, glucose transporter 2; GPCR, G-protein coupled receptor; Kv, voltage-gated potassium channel.