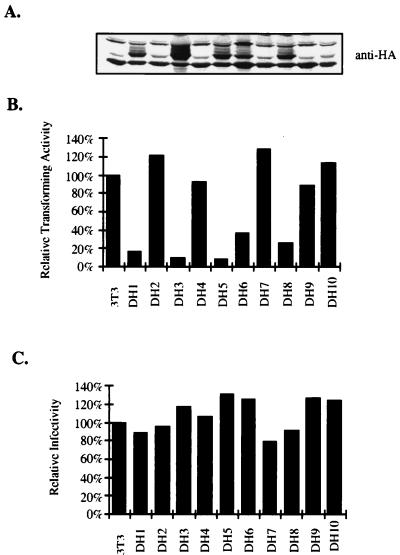
FIG. 9.
Overexpression of DOKL in NIH 3T3 cells represses v-Abl transforming activity. (A) Western blot analysis of DOKL expression. NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with pCGN-DOKL and a puromycin selection marker. Puromycin-resistant clones were picked, expanded, and analyzed for DOKL expression with anti-HA antibodies. Extracts from parental NIH 3T3 cells are also shown. Several lines expressing HA-tagged DOKL protein were identified. Lane designations match those for bars in panels B and C. (B) Transforming efficiencies of v-Abl on DOKL-overexpressing cell lines. Cell lines were infected with serially diluted v-Abl virus and plated in low-concentration serum, and the number of transformed foci on plates were scored. The titer of v-Abl virus, in focus-forming units (FFU) per milliliter, was determined for each cell line. The apparent viral titers for the cell lines relative to the apparent viral titer for parental NIH 3T3 cells (100% corresponds to 1.1 × 105 FFU/ml) are indicated. (C) Infectivities of pGDN virus on DOKL-overexpressing cell lines. Cell lines were infected with serially diluted pGDN virus and selected in G418-containing medium, and G418-resistant clones were scored. The apparent viral titers for the cell lines relative to the apparent viral titer for parental NIH 3T3 cells (100% corresponds to 7.7 × 105 FFU/ml) are indicated.