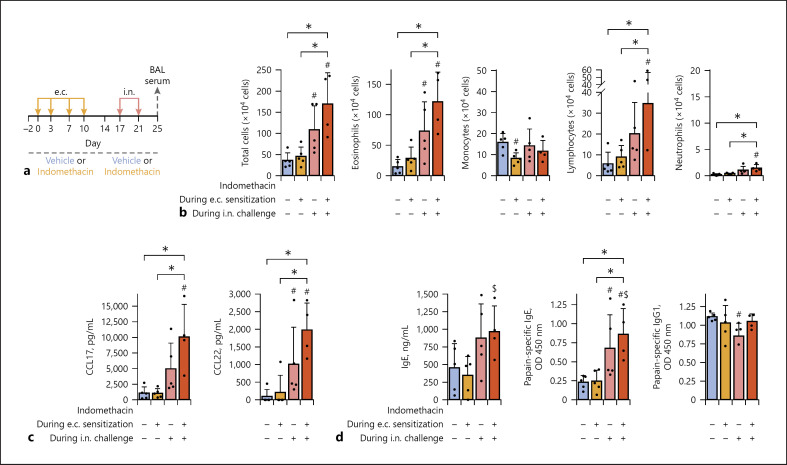
Fig. 3.
COX inhibition during the e.c. sensitization or i.n. challenge phase contributed to the enhancement of airway inflammation modestly or largely, respectively. Mice were administered with indomethacin or vehicle during e.c. sensitization, i.n. challenge, or both phases. All the animal groups were e.c. sensitized to 10 mg/mL papain via intact ear skin and subsequently i.n. challenged (2.5 μg papain). a Time line. b Airway inflammation. c Th2-attracting chemokines in BAL fluid. d Antibody responses. Data are indicated as the mean ± SD of 5 or 4 mice per group and are representative of 3 independent experiments with similar results. *p < 0.05 by ANOVA among the 4 animal groups. #p < 0.05 by the Mann-Whitney U test (vs. vehicle). $p < 0.05 by the Mann-Whitney U test (d: vs. indomethacin during e.c. sensitization). COX, cyclooxygenase; e.c., epicutaneous; BAL, bronchial alveolar lavage.