Fig. 1.
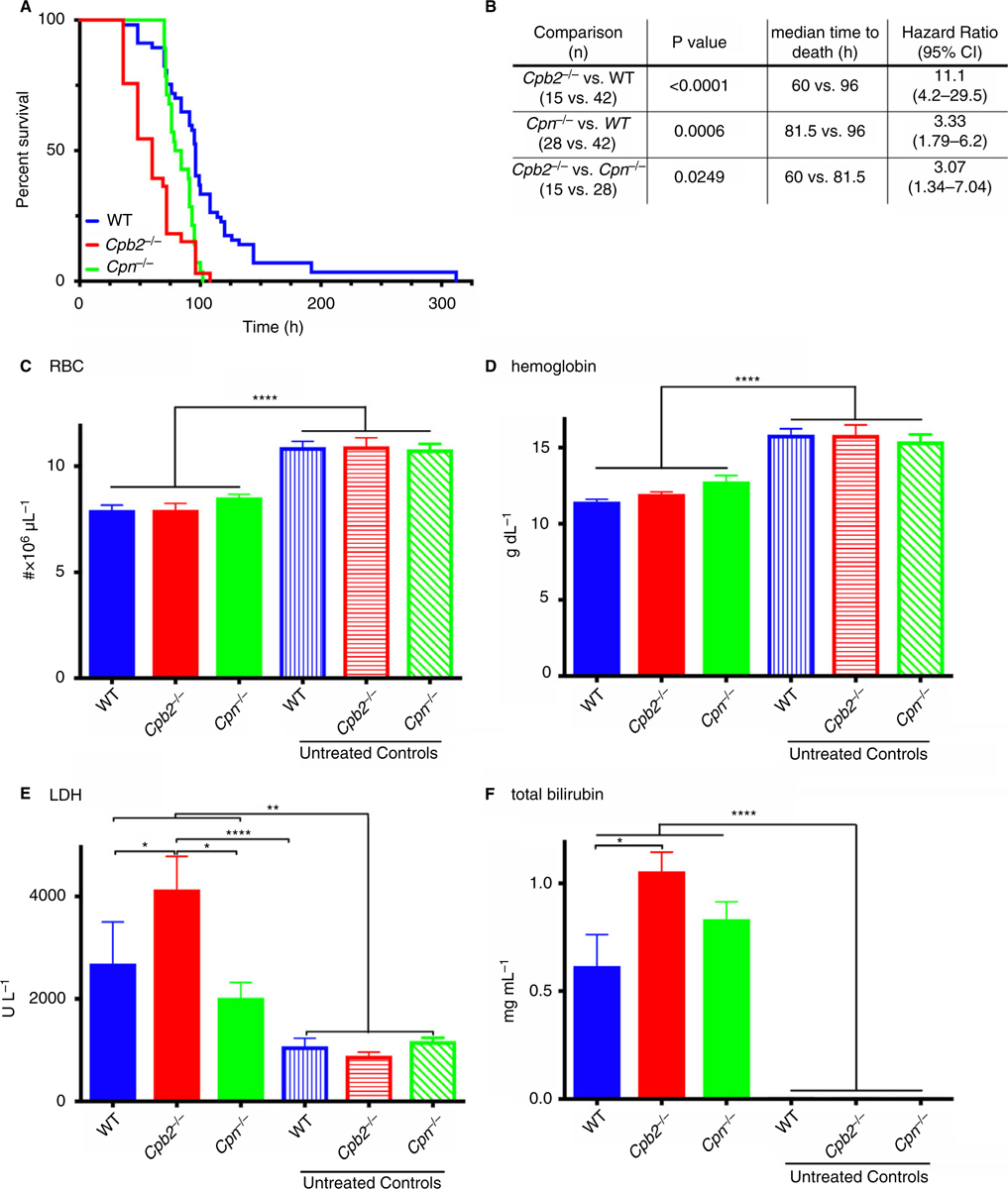
Cpb2−/− mice have exacerbated hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) compared with wild-type (WT) or Cpn−/− mice. Disease was induced by treatment with Stx2 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) together as described in Methods, and in C-F the mice were sacrificed at 48 h for blood collection (n = 10) for complete blood count (CBC) and clinical chemistry analysis. (A) Cpb2−/−, Cpn−/− and WT mice were followed until death (n = 15, 28 and 42, respectively). (B) Data analyzed by the log rank method with Bonferroni correction for multiple testing. Data analyzed by the log rank method (P = 0.0708). (C) red blood cell (RBC) count, (D) hemoglobin levels, (E) plasma lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and (F) plasma total bilirubin. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.
