Figure 1 .
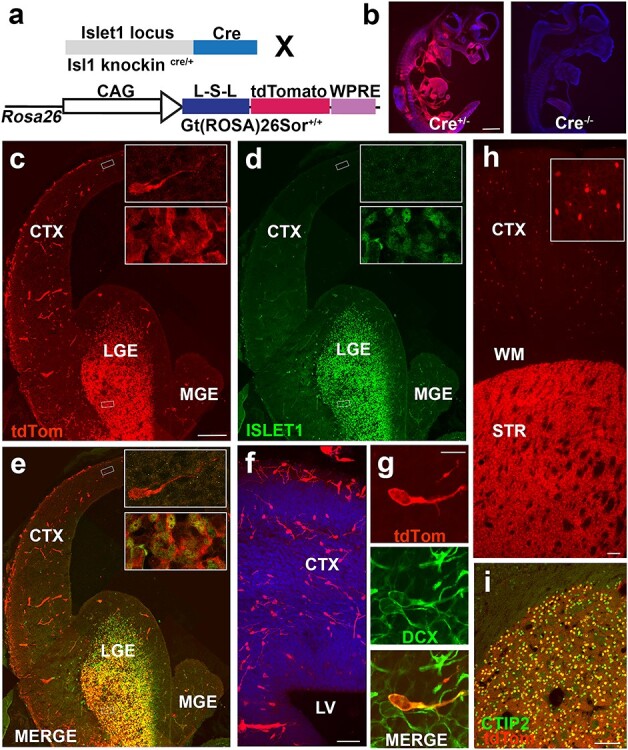
A subset of Isl1-derived tdTomato+ neurons tangentially migrate into developing neocortex. (a) Schematic of cross to identify lineage of Isl1 precursor cells. (b) TdTomato+ expression at E11.5 in Is1cre/+; 129S6-Gt(Rosa)26Sortm14(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J and Isl1+/+ and 129S6-Gt(Rosa)26Sortm14(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J mice indicate no tdTomato expression was observed in the absence of the Cre allele. (c–e) E14.5 mouse brain section indicating areas of (c) Isl1-derived tdTomato+ cells (d) ISL1, and co-expression (e) between the 2 populations in developing LGE. Insets depict example of bipolar migratory neuron in neocortex (upper inset) and cells in developing striatum (lower inset) corresponding with boxed regions in low mag. (f) Migrating tdTomato+ neurons crossing corticostriatal junction. Leading apical processes indicate direction of migratory stream from GE into neocortex. (g) TdTomato+ cell is co-positive for DCX confirming migratory immature neuron identity. (h) Low magnification image of tdTomato+ coronal section at P21 showing cortical and striatal labeled cells. Inset shows high magnification image of tdTomato+ neurons in cerebral cortex. (i) All tdTomato+ cells in striatum are CTIP2+ indicating a medium-sized spiny striatal projection neuron identity. CTX—cerebral cortex; LGE—lateral ganglionic eminence; MGE—medial ganglionic eminence; LV—lateral ventricle; WM—white matter; STR—striatum. Scale bars represent 1000 μm (b); 200 μm (c–e); 50 μm (f); 10 μm (g) ; 100 μm (h) and 100 μm (i).
