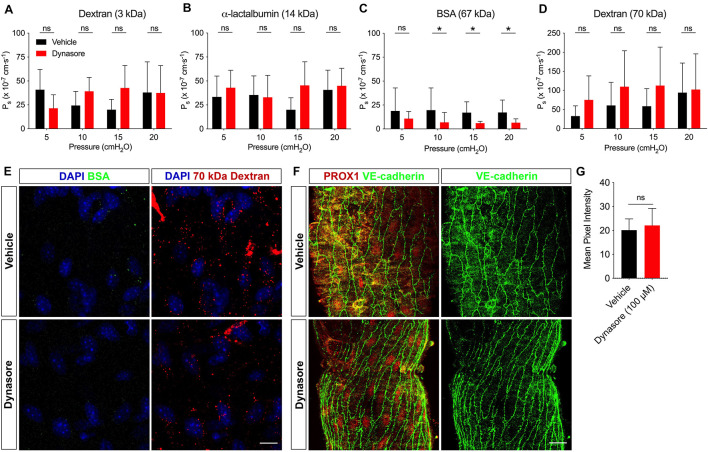
FIGURE 3.
BSA utilizes vesicular transport to cross the lymphatic barrier. Ps of collecting lymphatic vessels to (A) 3 kDa dextran (n = 7), (B) α-lactalbumin (n = 5), (C) BSA (n = 8), or (D) 70 kDa dextran (n = 8) was determined first in the presence of vehicle (black bars), followed by dynasore (red bars), an inhibitor of vesicle formation. (E) Collecting lymphatic vessels treated with either vehicle of dynasore (100 μM) and imaged immediately after perfusion of BSA-AF488 (green) and 70 kDa dextran (red). Vesicles containing BSA-AF488 and 70 kDa dextran-TR are visible in the endothelial layer. (F) Representative images of collecting lymphatic vessels stained for PROX1 (red) and VE-cadherin (green) after treatment with either vehicle or dynasore (100 μM) and imaged by confocal microscopy. (G) Summary data of mean pixel intensity from n = 3 pairs of isolated, immunostained lymphatic vessels treated as in D (Student’s unpaired t-test; P = 0.71). All graphs show mean ± SD and each “n” refers to a different mouse. *, P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA. Scale bar is 10 μm in panel (E) and 20 μm in panel (F).