Fig. 1. Simplified representation of the DNA-damage-induced checkpoint response.
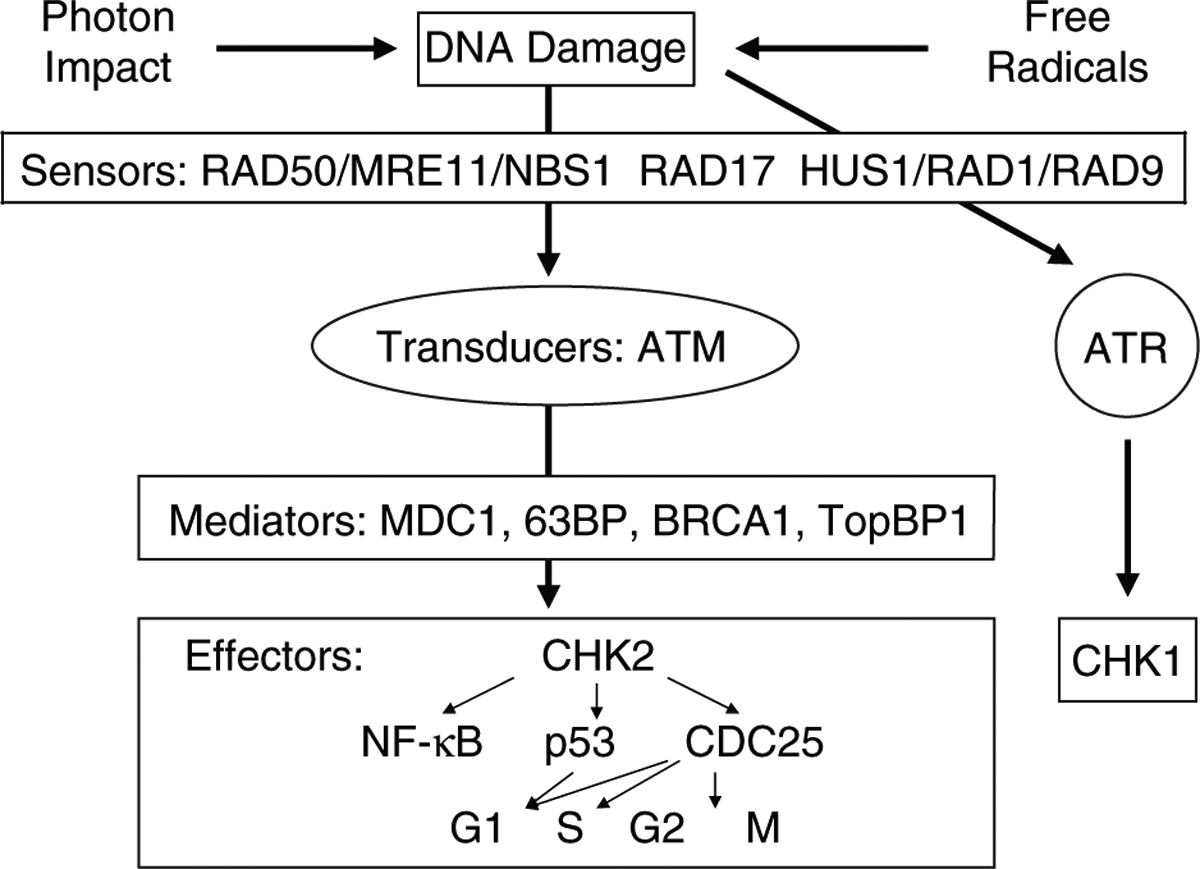
Ionizing radiation induces DNA breaks. After the detection of a given damage by sensor proteins, this signal is transduced to the effector protein CHK2 via the tranducer protein ATM. Depending on the phase of the cell cycle the cell is in, this can lead to activation of p53 and inactivation of CDC25, which eventually leads to cell cycle arrest. Mediator proteins mostly are cell cycle specific and associate with damage sensors, signal transducers, or effectors at particular phases of the cell cycle and, thus, help provide signal transduction specificity. The effect of UV light is via the transducer protein ATR and the effector protein CHK1. MRE11: meiotic recombination 11; NBS1: Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1; ATM: ataxia telangiectasa mutated; ATR: ataxia telangiectasa related; MDC1: mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1; 63BP: p63 binding protein; BRCA1: breast cancer 1; TopBP1: topoisomerase binding protein 1; CHK1: check 1; CHK2: check 2; CDC25: cell division cycle 25; G1: gap 1; S: synthesis; G2: gap 2; M: mitosis.
