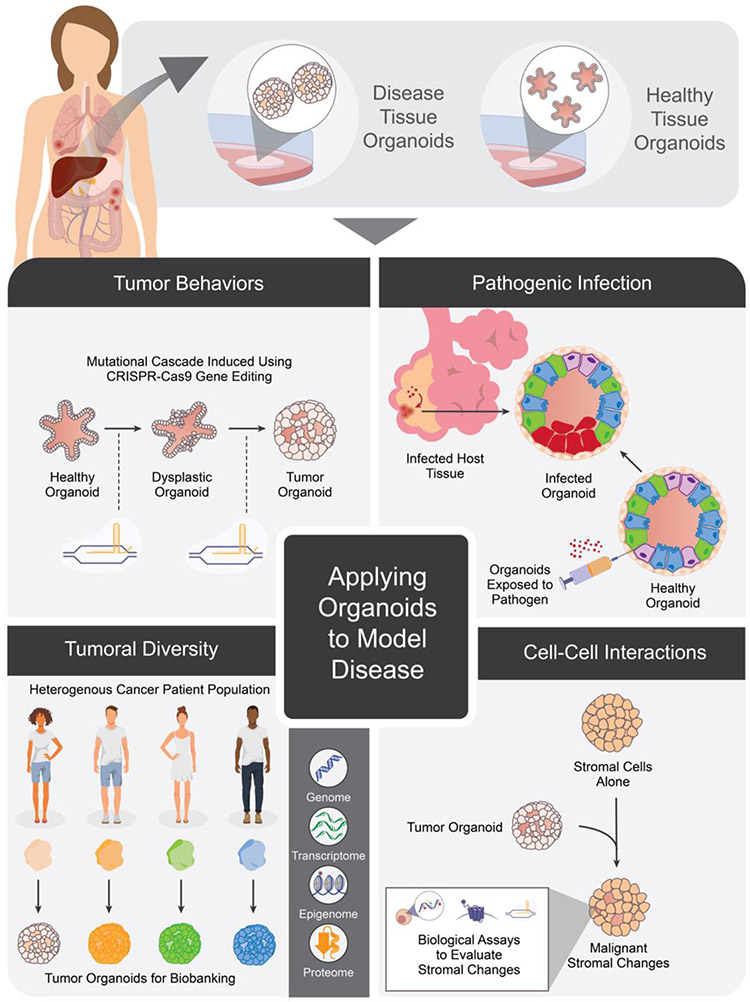
Figure 1: Organoids derived from healthy and diseased tissue can be used to model various aspects of human physiology.
These include (clockwise from top left) modelling mutational cascades involved in carcinogenesis, features of pathogenic viral and bacterial infections, capturing the heterogeneity of tumor genetic subtypes, and cell-cell interactions that promote malignant cellular characteristics.