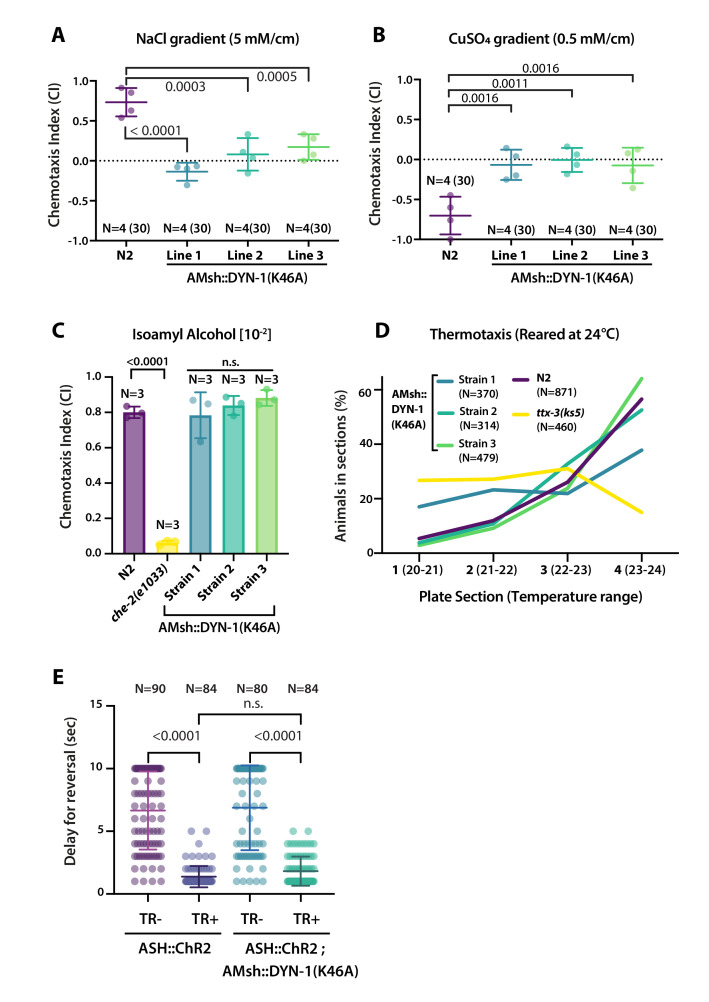
Figure 8. AMsh phagocytic activity affects ASER and ASH sensory functions.
(A) Chemotactic indexes of four independent assays made with 30 N2 or AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) transgenics in linear 5 mM/cm NaCl gradients. The chemoattraction to NaCl was lost in transgenics expressing AMsh::DYN-1(K46A). One-way ANOVA, multiple comparisons corrected by Tukey test. (B) Chemotactic indexes of four independent assays made with 30 N2 or AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) transgenics in linear 5 mM/cm CuSO4 gradients. Animals expressing AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) did not show avoidance behavior to CuSO4. One-way ANOVA, multiple comparisons corrected by Tukey test. (C) Chemotactic indexes of three independent assays made with an average of >100 N2, che-2, or AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) transgenics in a gradient of the volatile attractant isoamyl alcohol (IAA). The top of the gradient was spotted with [10–2] IAA. AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) did not affect IAA chemotaxis. One-way ANOVA, multiple comparisons corrected by Dunnett’s test. (D) Thermotactic behavior in one temperature gradient assays made with >400 N2, ttx-3(ks5) or AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) transgenics. AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) did not consistently affect thermotaxis. (E) Transgenic animals expressing ChR2(H134R) in ASH sensory neurons (ASH::ChR2(H134R); lite-1) exhibit fast reversal (minimum 1–2 backward head swings) in response to blue light exposure (15 mw/mm2). This response was only observed when animals were raised in the presence of trans-retinal (TR+). Control groups were done using the same strain and same stimulation but were raised in the absence of trans-retinal (-TR). Expression of AMsh::DYN-1(K46A) does not modify this avoidance response. Kruskal–Wallis test, multiple comparison corrected by Dunn’s test.