Figure 2.
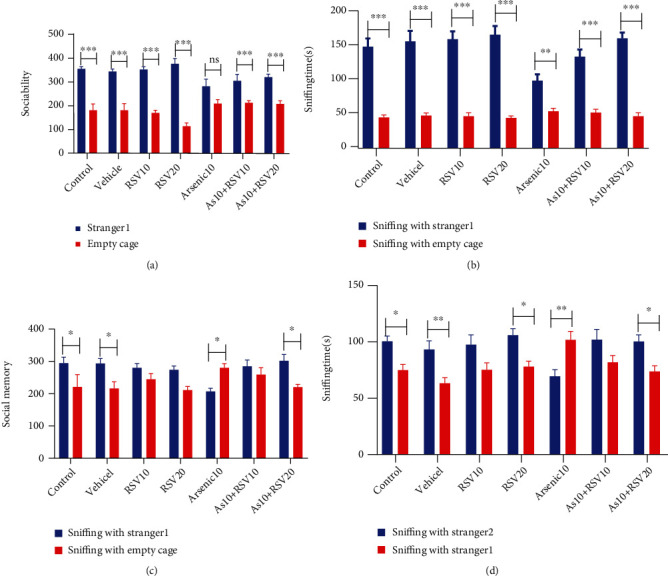
Social interaction task. Sociability: control, vehicle, RSV10, RSV20, As+RSV10, and As+RSV20 groups showed a higher interaction with stranger 1 compared to empty cage. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. control, vehicle, RSV10, and RSV20. ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. As+RSV10. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. As+RSV20 (a). There was also a significant difference in sniffing rate with stranger 1 compared to the empty cage in all groups. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 vs. control, vehicle, RSV10, RSV20, As+RSV10, and As+RSV20. ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. As (b). Social memory: there was a higher interaction with stranger 2 compared to stranger 1 in control, vehicle, and As+RSV20. In As group, rats showed a higher interaction with stranger 1 compared to stranger 2. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 vs. control, vehicle, and As+RSV20. ∗p < 0.05 vs. As (c). There was a higher sniffing rate with stranger 2 compared to stranger 1 in control, vehicle, RSV20, and As+RSV20 groups. There was a higher sniffing rate with stranger 1 compared to the new one in As rats. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 vs. control, RSV20, and As+RSV20. ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. vehicle and As (d).
