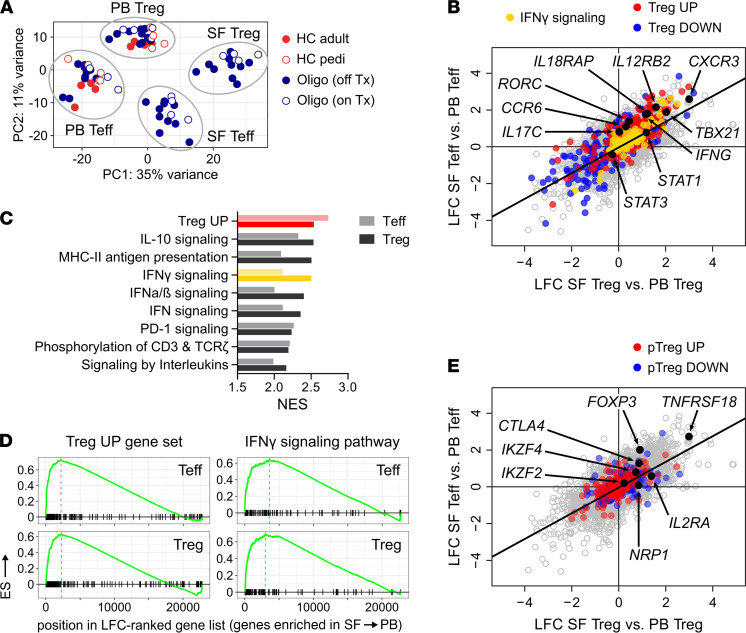
Figure 3. Teffs and Tregs in oligo JIA SF upregulate IFN-γ–related genes.
Tregs (CD4+CD25+CD127lo) and Teffs (CD4+CD25–) were sorted from paired SF and PB samples of JIA patients (n = 14) and from the PB of pediatric (n = 5) and adult (n = 4) controls. (A) Principal component (PC) plot based on analysis of complete transcriptomes. (B) Log2 fold change (LFC) in gene expression derived from independent differential gene expression analyses of SF Tregs versus PB Tregs (x axis) and SF Teffs versus PB Teffs (y axis). Genes of the IFN-γ signaling pathway (Reactome database) and Treg signature (30) are color-coded. Selected Th1- and Th17-related genes are annotated. (C) Normalized enrichment score (NES) of top hits in gene set enrichment analyses (GSEAs) of Treg and Teff subsets (see Supplemental Table 4 for complete GSEA results). (D) Running enrichment scores for the set of genes upregulated in classical Tregs (30) and for the IFN-γ signaling pathway (Reactome database). (E) LFC in gene expression derived from differential gene expression analysis of Treg (x axis) and Teff (y axis) subsets. Genes of the peripherally induced Treg (pTreg) signature (29) are color-coded. Selected Treg-related genes are annotated. HC, healthy control; pedi, pediatric; oligo, oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Tx, treatment.