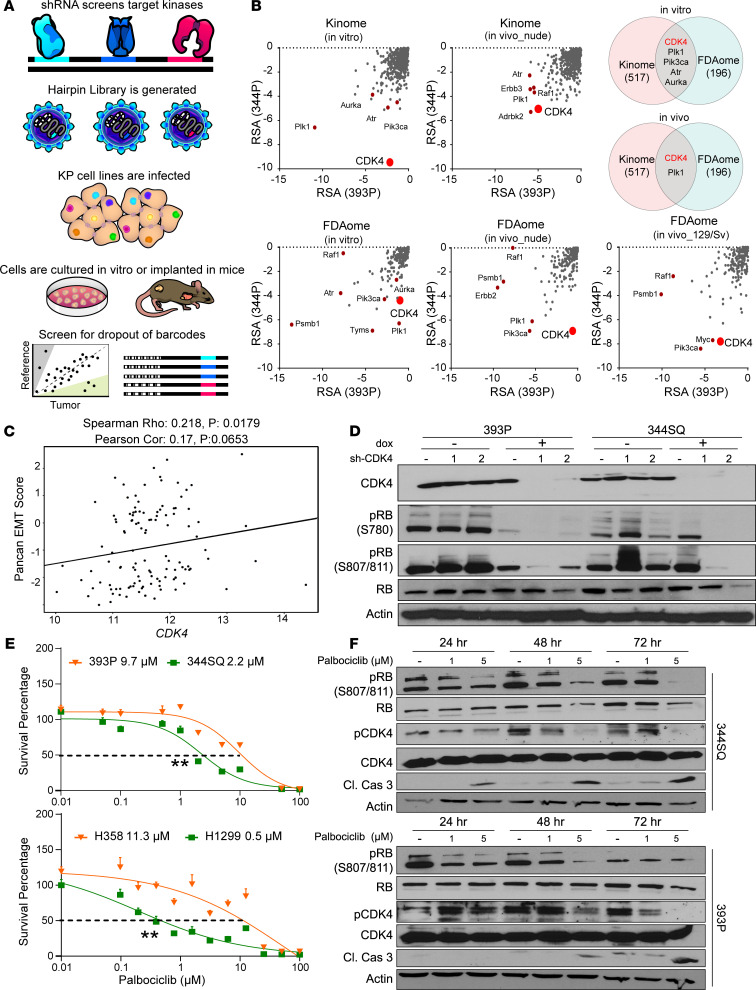
Figure 1. Mesenchymal lung cancer cells exhibit increased dependency on CDK4 for growth.
(A) Schematic illustration of the workflow of the shRNA dropout screens. A library of lentiviral particles expressing 10 different barcoded shRNAs was transduced into murine KP-mutant lung cancer cells. The cells were cultured in vitro or implanted in nude or syngeneic 129/Sv mice and later sequenced for barcoded shRNAs and compared with reference cells. (B) Results from Kinome and FDAome shRNA dropout screens in 393P and 344P cell lines and tumors compared based on the redundant shRNA activity (RSA). Top differential hits are labeled on the graphs, most important being CDK4. Venn diagram shows comparisons across different conditions and top hits identified. (C) Cluster plot analysis of correlation between EMT score and CDK4 mRNA expression of 118 human NSCLC cell lines. (D) Western blot analysis of CDK4 pathway after 6 days of CDK4 knockdown. (E) In vitro cell viability after 48-hour palbociclib treatment in a panel of epithelial and mesenchymal murine (393P, 344SQ) and human (H358, H1299) lung cancer cell lines. n = 8 per drug concentration. The curve was generated using a nonlinear regression fit model. Vertical error bars shown. **P < 0.001, 2-tailed Student’s t test. (F) 344SQ and 393P cells were treated for 24, 48, and 72 hours with 1 and 5 μM palbociclib, and Western blot analysis was utilized to demonstrate drug efficacy over a dose range. Cleaved caspase-3 was used as an apoptotic marker.