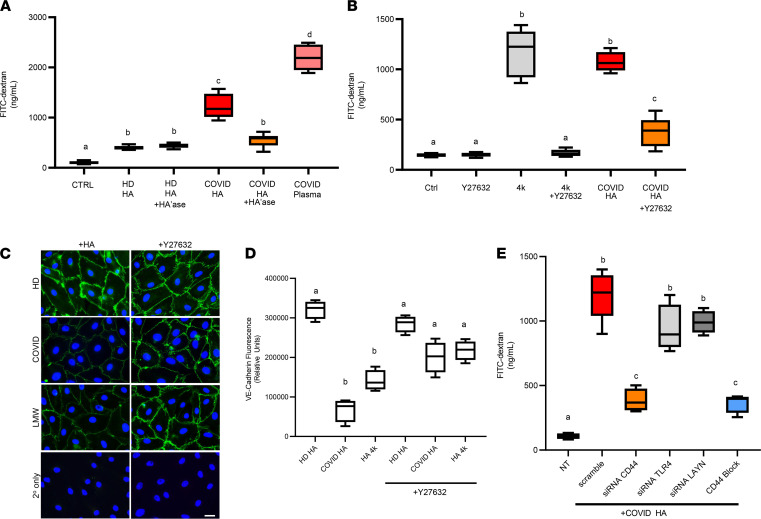
Figure 6. HA fragments present in COVID-19 plasma promote endothelial dysfunction.
(A) LMVEC were seeded on permeable supports (3 μm pore size) placed into a 24-well plate and grown to confluence. Cells were treated with or without HA purified from patient plasma samples (750 ng HA) or 1.5% patient plasma for 16 hours at 37°C to induce endothelial barrier disruption. The upper chamber was replaced with FITC-conjugated dextran (1 mg/mL, 40 kDa) in PBS, and medium from the lower chamber was measured after 1 hour. (B) LMVECs were grown to confluence in a transwell chamber and coincubated in the presence or absence of the ROCK inhibitor Y27632 (10 μM), in the presence or absence of biosynthetic 4 kDa HA (1000 ng), or in the presence or absence of HA purified from patient plasma for 16 hours at 37°C to induce endothelial barrier disruption, and barrier function was measured as above. (C) LMVEC were grown on coverslips until confluency in the presence or absence of Y27632 prior to treatment with either HA purified from healthy donor plasma, COVID-19 patient plasma, or LMW-HA (4 kDa). Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with an antibody against VE-cadherin. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) VE-Cadherin immunostaining was quantified by using 3 independent experiments and normalized to the number of endothelial cells per field using ImageJ. (E) LMVECs were treated for 48 hours in the presence or absence of siRNA (10 nM) or a CD44-HA blocking antibody (KM114, 1 μg) prior to treatment with HA and measurement of barrier function. In some experiments, HA was digested with Streptomyces hyaluronidase (HA’ase) as a specificity control. Data are reported as mean ± SEM; n = 5 independent experiments of at least 4 patients each, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests. Different alphabetical superscripts are significantly different from each other; P < 0.05.