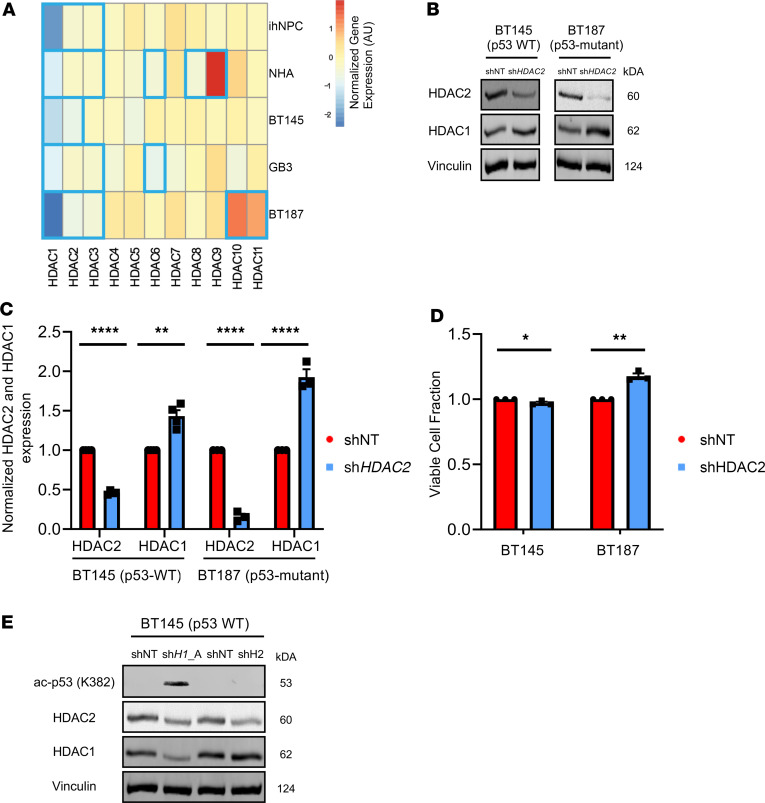
Figure 3. HDAC1 function is nonredundant in hGSCs and is not compensated for by its paralogue HDAC2.
(A) Log2 fold change of differential expression for the 11 HDACs (HDAC1–11) after short hairpin HDAC (shHDAC1) knockdown in 2 nontumorigenic (ihNPC and NHA) and 3 hGSC (BT145, GB3, BT187) cell lines. Blue bolded boxes indicate significant differential expression (adjusted P ≤ 0.05). (B) Representative immunoblot showing protein levels of HDAC1 and HDAC2 after acute HDAC2 knockdown (shHDAC2) in p53-WT (BT145) and p53-mutant (BT187) hGSCs. (C) Quantification of expression of HDAC2 and HDAC1 protein (normalized to Vinculin) after HDAC2 knockdown in BT145 (n = 4) and BT187 (n = 3). (D) Quantification of the percentage of viable hGSCs (BT145 and BT187) 7 days after HDAC2 knockdown, relative to shNT controls (n = 3). (E) Immunoblot comparing levels of acetylated p53 (K382) and HDAC1 and HDAC2 protein after HDAC1 and HDAC2 silencing in p53-WT hGSCs (BT145). For each cell line, the data are compiled from at least 3 independent experiments for each shRNA. Error bars indicate SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. P values were calculated using unpaired 2-tailed t test. See also Supplemental Figure 4.