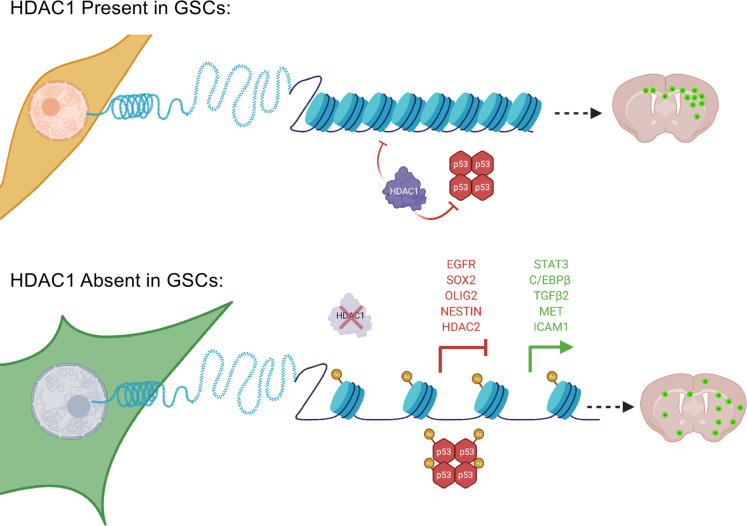
Figure 8. Proposed model: consequences of HDAC1 silencing in p53-WT hGSCs.
Summary of the cellular and molecular effects of HDAC1 loss in p53-WT hGSCs. Absence of HDAC1 results in increased histone acetylation and restoration of p53 activation and stability. These changes are accompanied by marked changes in gene expression, wherein genes involved in maintaining stemness are downregulated while genes involved in promoting differentiation and cellular migration and communication are upregulated. In vitro, these cells fail to proliferate and die; however, when transplanted in vivo these cells form slower growing but more invasive tumors. STAT3 activity, which is known to drive aggressive phenotypes in GBM, is upregulated after HDAC1 loss and may be a potential druggable compensatory pathway that may be targeted in combination with more selective HDAC1i.