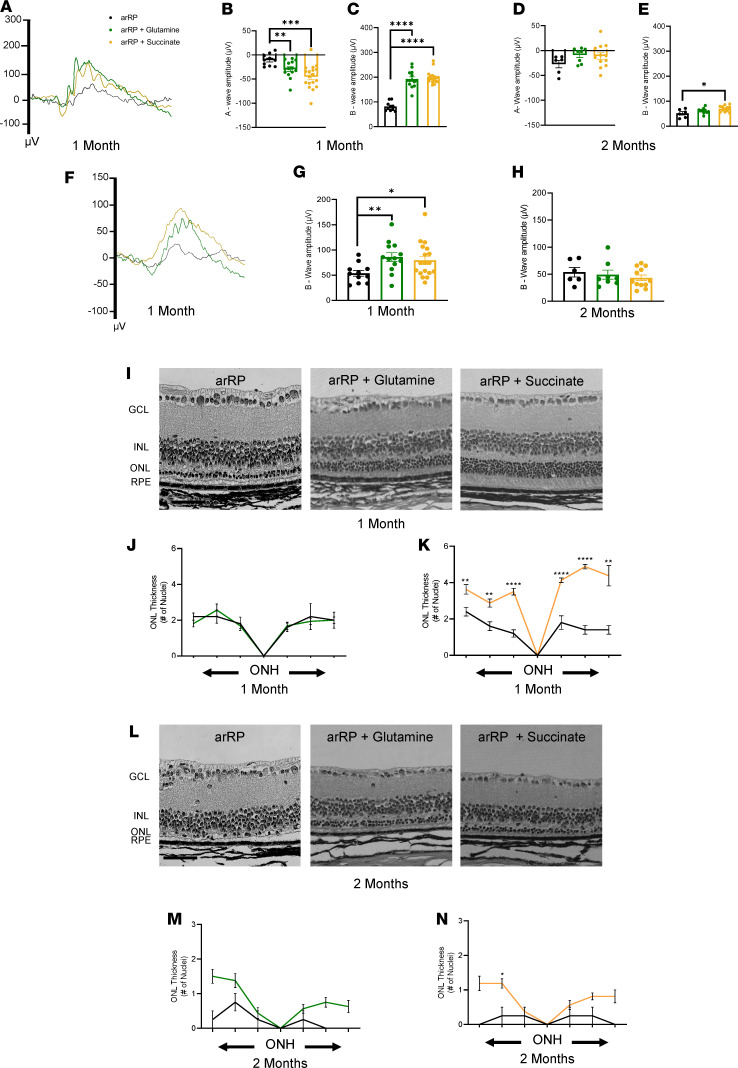
Figure 4. Succinate supplementation provides resilience against cell death for the photoreceptors and prolongs visual function.
(A) Representative average ERG traces for untreated arRP mice (black) and arRP mice treated with glutamine (green) or succinate (yellow) recorded at a 2.5 log cd•s/m2 flash intensity. (B) Quantification of the a-wave (C) and b-wave amplitude for both glutamine-treated arRP mice and succinate-treated arRP mice compared with untreated arRP mice. (D) By 2 months of age, no significant change was detected in the a-wave response for either succinate or glutamine treatment, (E) but succinate-treated arRP mice showed an increase in b-wave response. (F) Representative average ERG traces for untreated arRP mice and arRP mice treated with glutamine or succinate recorded at a –1.1 log cd•s/m2 flash intensity. (G) Quantification of the b-wave amplitude shows a significant increase for arRP mice treated with glutamine or succinate at 1 month (H) but shows no detectable increase by 2 months of age. n ≥ 5 eyes. (I) Histology of the arRP retinas treated with either glutamine or succinate compared with untreated arRP retinas at 1 (L) and 2 months of age. Scale bar: 50 μm. (J and K) Morphometric quantification of ONL thickness spanning from the ONH at 1 (M and N) and 2 months of age. n = 3 eyes each group, with multiple counts per eye. ONL Thickness was analyzed by multiple 2-tailed t tests with the Holm-Sidak method to correct for multiple comparisons. ERG data were analyzed by student’s t test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. ERG, electroretinogram; arRP, autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa; GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ONH, optic nerve head.