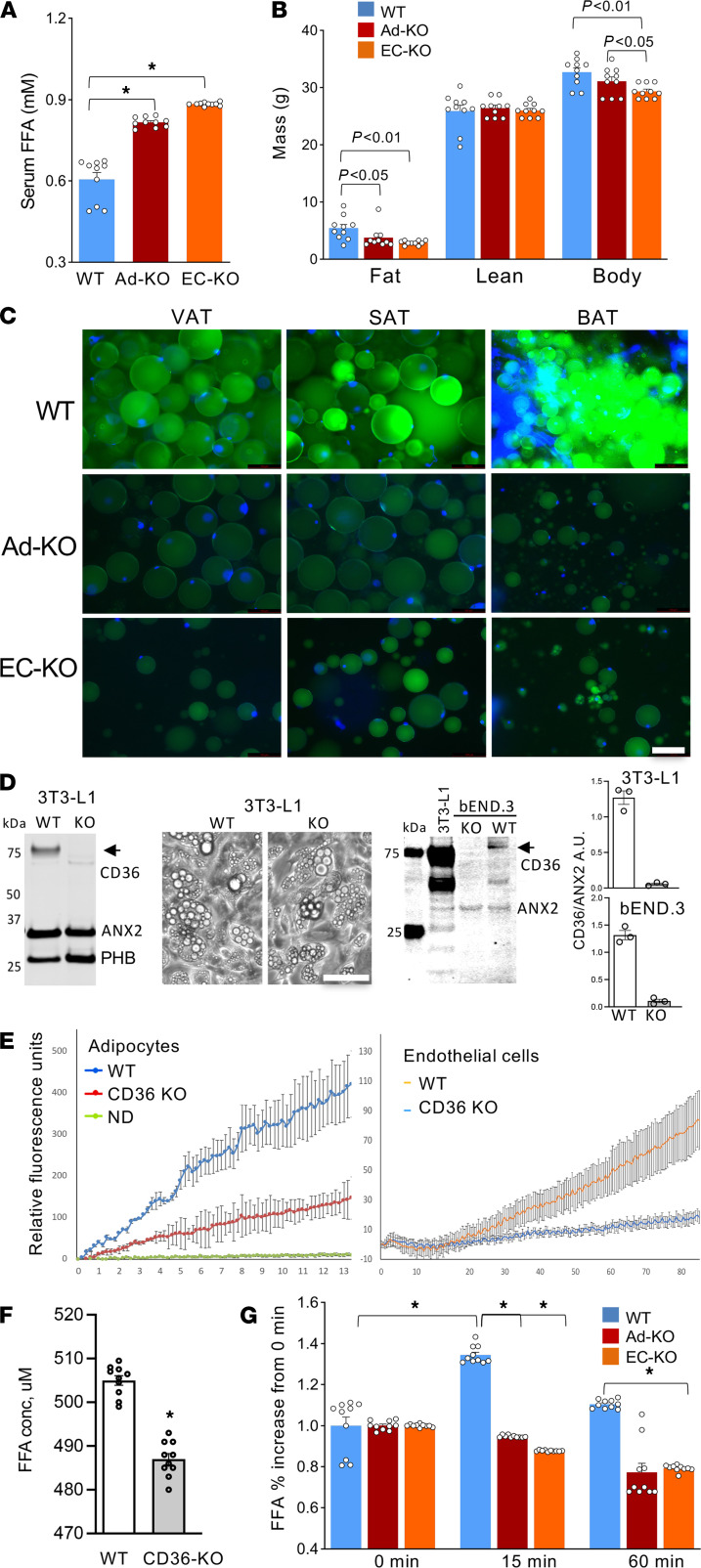
Figure 1. CD36 in adipocytes and the endothelium mediates LCFA transport in adipose tissue.
(A) Steady-state plasma concentration of free fatty acids (FFAs), higher in CD36 EC-KO and Ad-KO mice. n = 10 mice. (B) Body composition measured with EchoMRI and body weight (BW) revealed reduced adiposity in CD36-KO mice (n = 10 mice, 1-way ANOVA). (C) Reduced BODIPY-C16 uptake by adipocytes in CD36 Ad-KO and EC-KO mice. Visceral adipose tissue (VAT), subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT), and brown adipose tissue (BAT) were recovered 180 minutes after i.v. BODIPY-C16 injection and green fluorescence was imaged in cell suspension upon tissue digestion with collagenase. Scale bar: 50 μm; blue: DNA. (D) Western blotting confirmed KO of CD36 in 3T3-L1 cells. Images: lipid droplet formation in control and CD36-KO adipocytes differentiated for 5 days. Western blotting on proteins extracted from control and CD36-KO bEND.3 cells demonstrated loss of CD36, but not of PHB and ANX2, immunoblotted for as loading controls. Arrow: glycosylated CD36. Arrowhead: nonglycosylated CD36. Graphs: Western quantification in AU. Scale bar: 50 μm for all panels. (E) QBT assay demonstrating that LCFA uptake by CD36-null 3T3-L1 adipocytes and bEND.3 cells was inefficient compared with nondifferentiated (ND) cells. n = 5 wells. (F) Concentration of FFA in culture medium 3 hours after lipolysis induction in WT and CD36-null 3T3-L1 adipocytes (n = 10 wells, Student’s t test). (G) Relative increase in plasma concentration of FFA 15 minutes after isoproterenol injection observed in WT but not CD36-KO mice (n = 10 mice, 1-way ANOVA). In all panels, data are shown as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.01.