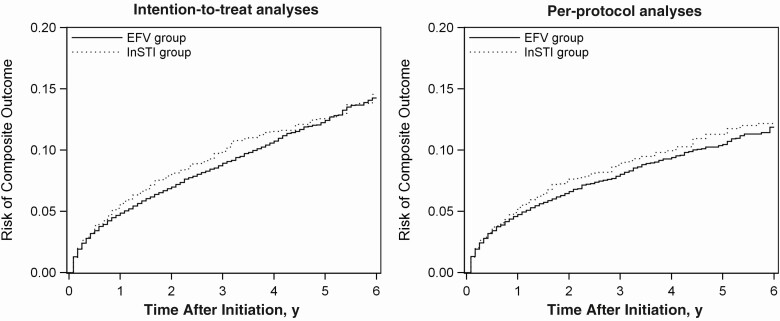
Figure 1.
Risk of the composite outcome (AIDS-defining illnesses, acute myocardial infarction or stroke, end-stage renal disease, end-stage liver disease, or death) among 15 993 human immunodeficiency virus–infected adults initiating an integrase strand transfer inhibitor (InSTI)–based or an efavirenz (EFV)–based regimen between July 2009 and December 2016 in the North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design. Left, Intention-to-treat analyses that accounted for baseline confounding and differential loss-to-follow-up. Right, Per-protocol analyses that accounted for baseline confounding, differential loss to follow-up, and treatment changes.