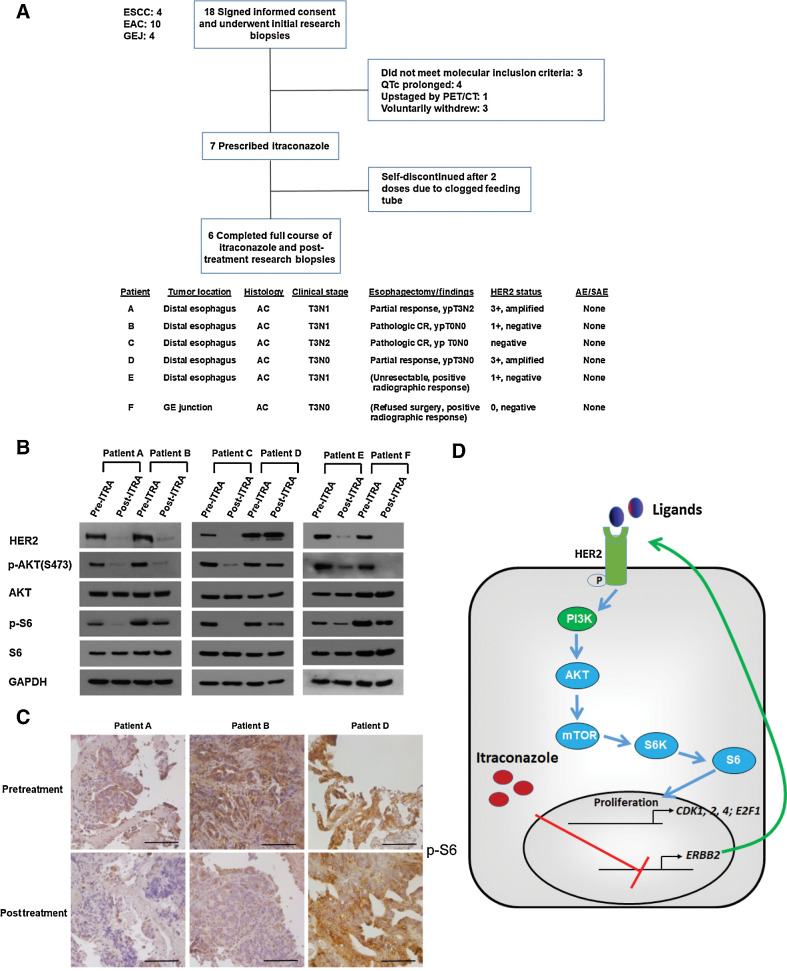
Figure 6.
Itraconazole inhibits HER2/AKT signaling in primary tumors from patients with esophageal cancer. A, Top, CONSORT diagram of early phase I trial. Eighteen patients with ESCC, EAC, or gastroesophageal junction cancer signed written informed consent and were enrolled in the trial. Following initial research biopsies but before itraconazole was prescribed, 11 patients screen failed or voluntarily withdrew. Seven patients were prescribed itraconazole, with one patient discontinuing the medication after only 2 doses. Bottom: clinical and pathologic characteristics of the 6 patients who completed the full course of itraconazole. B, Western blot analysis of p-AKT, AKT, p-S6, S6, and HER2 protein in primary tumors from 6 patients with esophageal cancer before and after itraconazole treatment. GAPDH is used as a loading control. C, IHC staining of p-S6 from representative tumor sections of three different patients before (top) and after (bottom) itraconazole treatment. Patients A and B responded while patient D minimally responded. Scale bar, 100 μm. D, Schematic diagram of itraconazole's action in esophageal cancer. HER2 functional activation promotes PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6 signaling, leading to the upregulation of AKT signaling target genes CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, and E2F1. Itraconazole suppresses this signaling pathway through downregulating ERBB2 mRNA.