Figure 1.
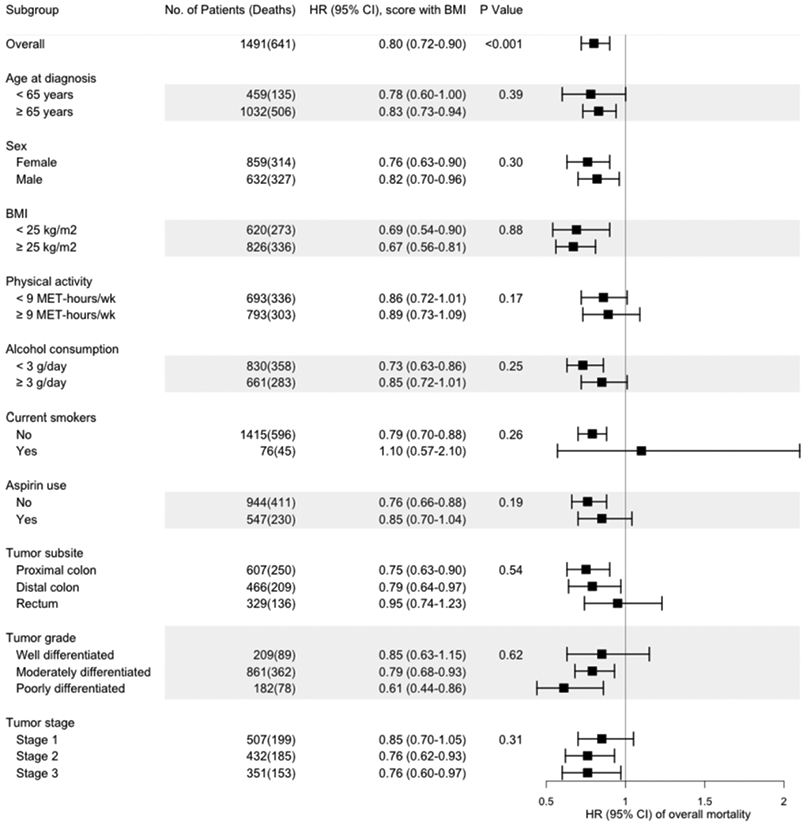
Multivariable hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) of overall mortality per IQRa increase in the post-diagnostic WCRF/AICR lifestyle score with BMI, stratified by demographic, lifestyle, and other factors and tumor characteristics.
The hazard ratios (HRs) for the post-diagnostic WCRF/AICR lifestyle score with BMI are indicated by solid squares; the 95% CIs are indicated by horizontal lines. Models were stratified by age at diagnosis (<65, ≥65 years) and tumor stage (I, II, III, and unspecified), with adjustment for age at diagnosis (continuous), cohort (NHS, HPFS), tumor grade (well differentiated, moderately differentiated, poorly differentiated, and unspecified), tumor subsite (proximal colon, distal colon, rectum, and unspecified), year of diagnosis (continuous), regular sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy screening (yes, no), post-diagnostic total energy intake (continuous), post-diagnostic regular use of aspirin (yes, no), and post-diagnostic smoking status (current, non-current), except in models stratified by these variables. P-values for interaction were calculated by the likelihood ratio test.
aIQR (interquartile range) of the post-diagnostic WCRF/AICR lifestyle score with BMI in NHS=0.89 and in HPFS=0.64.
