Figure 4. The effect of glycosylation on MuSK and AChR-specific human monoclonal antibody binding properties.
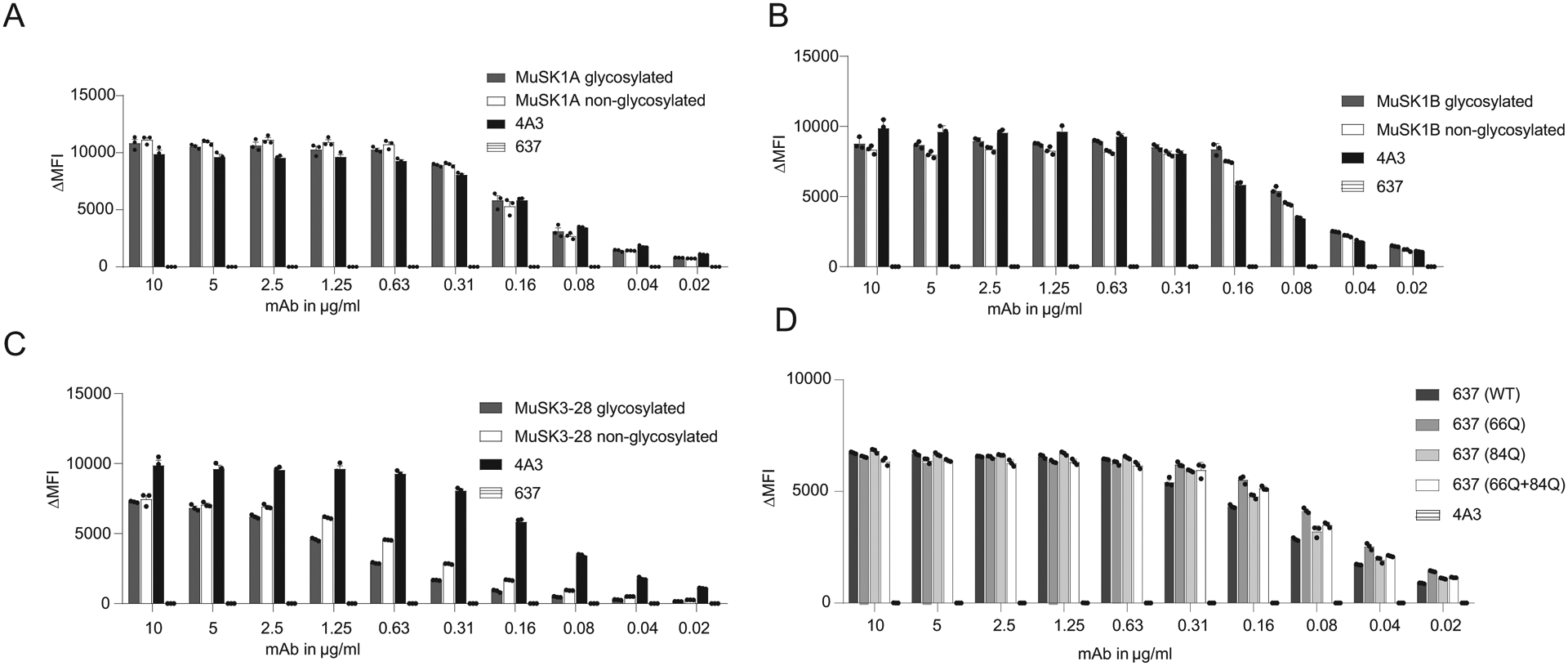
Antigen binding of three MuSK monoclonal antibodies (mAb) and one AChR-specific human mAb is not affected by the presence of variable region N-linked glycans. Wildtype MuSK and AChR mAbs and their glycovariants were tested for surface binding to MuSK or AChR with live cell-based assays (CBA) using MuSK-GFP-transfected (A-C) or AChR and rapsyn-GFP-transfected (D) HEK293T cells. All wildtype mAbs and their variants were analyzed in a two-fold dilution series. In the MuSK CBA (A-C), humanized MuSK-specific mAb 4A3 was used as the positive control and human AChR-specific mAb 637 as the negative control. In the AChR CBA (D), the MuSK-specific mAb 4A3 was used as the negative control. Each data point represents the mean value from three independent experiments, and error bars represent SDs. The ΔMFI was calculated by subtracting the signal from non-transfected cells from that of the transfected cells.
