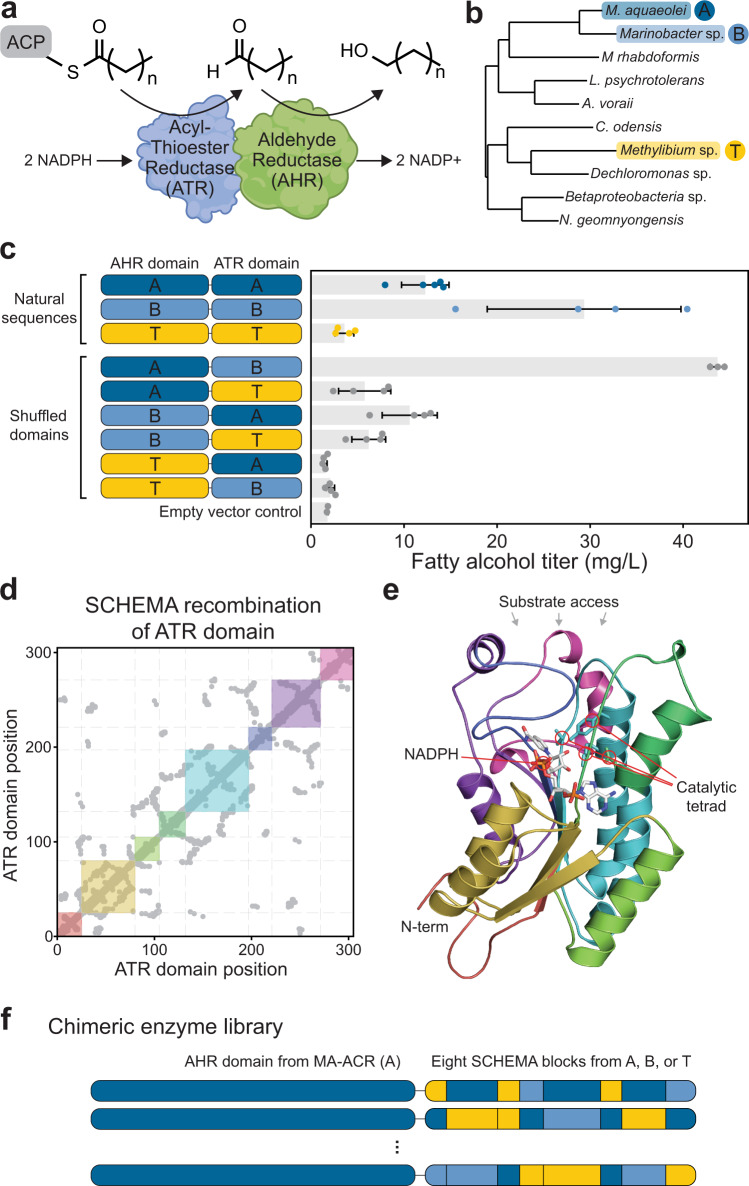
Fig. 1. Acyl-ACP reductase activity of natural and chimeric enzymes.
a Alcohol-forming acyl-ACP reductases consist of two domains that sequentially reduce acyl-ACP substrates to aldehydes, and then aldehydes to alcohols. b We focused our studies on three diverse sequences from M. aquaeloei (dark blue), Marinobacter BSs20148 (light blue), and Methylibium Sp. T29 (yellow), which we refer to as A, B, and T, respectively. c Total fatty alcohol production by the three natural sequences and the six chimeric enzymes generated by shuffling their AHR and ATR domains. The error bars represent one standard deviation centered at the mean of four replicates (n = 4) from cultures derived from individual colonies, except for MA-ACR (where n = 5), parent B (fusion A-B, where n = 3) and the empty vector (n = 2). d ATR domain residue-residue contact map used for SCHEMA recombination. The colored squares depict the eight sequence blocks from the SCHEMA design that minimize structural disruption. e The SCHEMA blocks mapped onto the ATR domain’s three-dimensional structure (the colors correspond to the squares in (d)). f Our chimeric ATR library was fused to the AHR domain from MA-ACR. Source data underlying Fig. 1c are provided as a Source Data file.