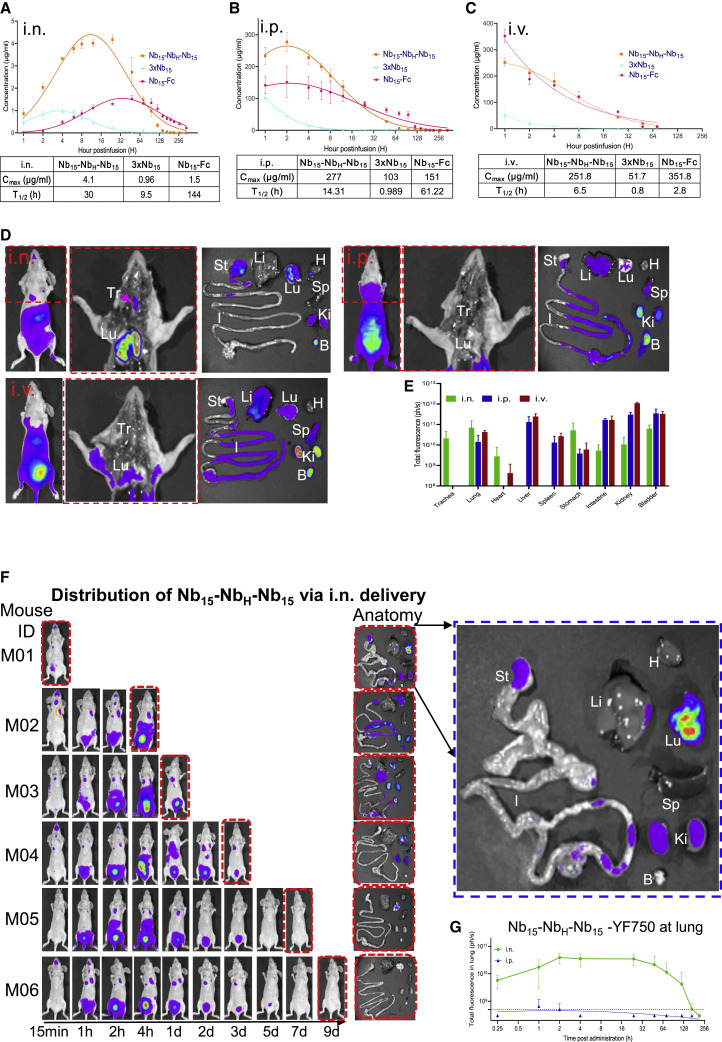
Figure 4.
Pharmacokinetics of Nb15s in vivo
(A–C) Bioavailability and T1/2 (half-life) of Nb15s in BALB/c mice. Nb15 variants were intranasally (i.n.) administered into mice (n = 3, female) at 200 μg (average of 10 mg/kg mice) (A), intraperitoneally (i.p.) administered into mice (n = 3, female) at 400 μg (average of 20 mg/kg mice) (B), and intravascularly (i.v.) administered into mice (n = 3, female) at 400 μg (average of 20 mg/kg mice) (C). Serum concentrations of the Nbs were determined at indicated time points by ELISA. Nb15 variants are colored as follows: Nb15-Fc (red), Nb15-NbH-Nb15 (orange), and 3 × Nb15 (cyan). Cmax, maximum observed plasma concentration. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(D) Spatial distribution of Nb15-NbH-Nb15YF750 1 h after infusion into mice (n = 3 in each group) by i.n., i.p., and i.v. routes was detected by a NightOwl LB 983 system. The middle figure in the red dashed line shows the dissected image of the left mouse in the red dashed line. The right figure shows the organs from dissected mice that were imaged immediately after sacrifice. Tr, trachea; Lu, lung; H, heart; Li, liver; Sp, spleen; St, stomach; I, large and small intestine; Ki, kidneys; B, bladder.
(E) The fluorescence intensity (ph/s) summary of each organ in (D) was quantified and presented as the mean ± SEM.
(F) Pharmacokinetics of Nb15-NbH-Nb15-YF150 by i.n. administration at the indicated time point. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated time point for the analysis of fluorescence intensity in various organs labeled as in (D). The blue dashed line figure shows the enlarged image of the individual figure indicated by corresponding arrows.
(G) Nude mice (n = 3–6) were administered with Nb15-NbH-Nb15-YF750 by the i.n. or i.p. route. The fluorescence intensity at the lung location as shown in the yellow dashed line circle of M02 in (F) was measured at the indicated time point. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.