Figure 2.
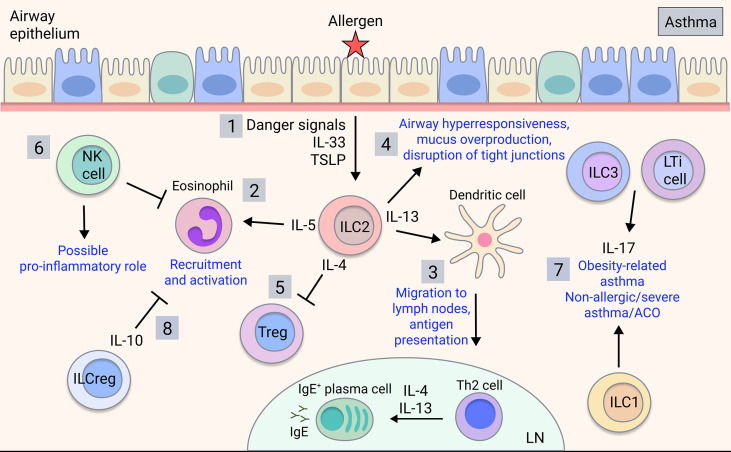
ILC involvement in asthma. Upon allergen detection by airway epithelium, 1) ILC2s are activated by signals released by the airway epithelial cells and other activated immune cells, producing type 2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in allergic asthma. 2) IL-5 is key for eosinophil recruitment and activation in the lung (77) and 3) IL-13 mediates dendritic cell migration to the lymph nodes, promoting T cell differentiation into effector Th2 cells, which mediate B cell class-switching and IgE production (78). 4) ILC2-derived IL-13 also acts on the airway epithelium to induce airway hyperresponsiveness, mucus overproduction and disruption of barrier integrity (43, 79, 80). 5) ILC2-derived IL-4 may potentially inhibit Treg production in asthma (81). 6) NK cells play an ambiguous role in asthma with both disease-driving and disease-modulatory activity shown. 7) ILC3s/LTi cells and possibly ILC1s contribute to obesity-related asthma and potentially non-allergic, severe asthma or ACO through production of IL-17 (82). 8) ILCregs may regulate asthma by inhibiting eosinophil recruitment through IL-10 (83).