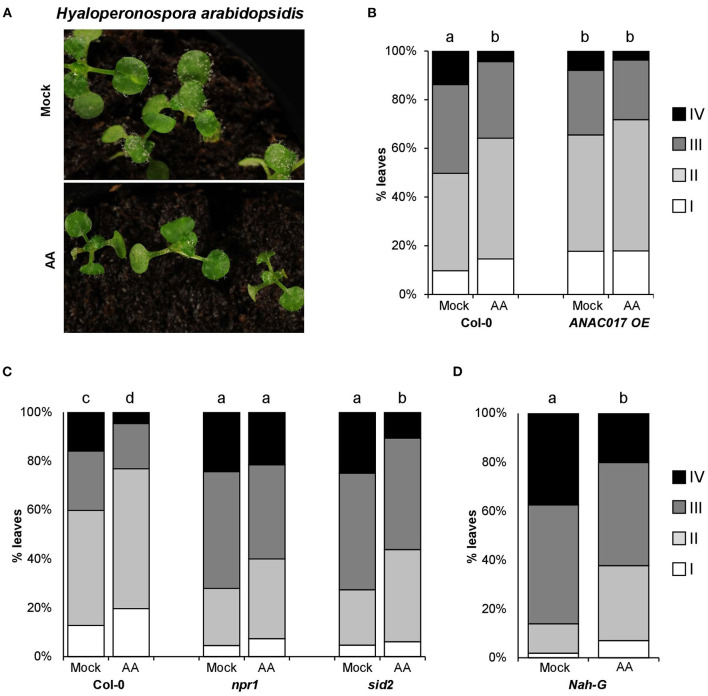
Figure 1.
Hpa resistance induced by antimycin A treatments. About 2.5-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings were treated with 50-μM antimycin A (AA) or control (Mock) +0.02% tween 20 by spray. Three days after treatment (dat), plants were spray inoculated with Hpa at 105 spores/ml. (A) Photographs showing AA-IR against Hpa 5 days post inoculation (dpi). (B–D) AA-induced resistance in different genetic backgrounds. For all genotypes, Hpa susceptibility was determined 5 dpi (and 8 dat). The plants were collected in ethanol 96% and trypan blue stained. Infected leaves were analyzed with the help of a stereomicroscope and assigned to one of the four different Hpa colonization classes (I: no visible colonization, II: Oomycete growth without sporulation, III: visualization of sporangiophores and asexual sporulation, IV: sexual sporulation). The bar graphs represent the classes distribution in % for the infected leaves analyzed in each genotype. The letters above the bars indicate statistically significant differences by multiple chi-square tests p ≤ 0.01. n = 150 (in D) −590 (in B and C).