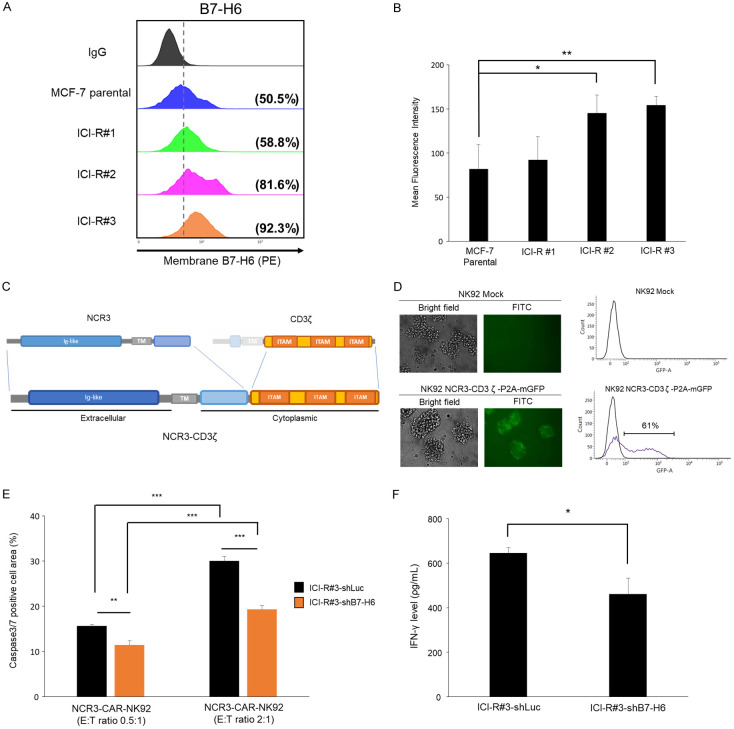
Figure 3.
Increased B7-H6 expression of ICI-R cells serve as a target of NCR3- NK92 cells. A. B7-H6 surface expressions of MCF-7 parental and the ICI-R derivatives were assessed by flow cytometry. B. The mean fluorescent intensity obtained by flow cytometry. Results are presented as mean ± SD based on three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by t-test: *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01. C. Schematic diagram of the NCR3-CD3ζ-P2A-GFP construct in a retroviral vector. The extracellular, transmembrane (TM), cytoplasmic regions, and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAM) are indicated. D. Left, the transduction efficiency of the CAR construct to NK92 cells was analyzed with the mGFP reporter by flow cytometry. Right, the plots of fluorescence intensities of the mock treated or virus-transduced NK92 cells. E. Cytotoxicity of NCR3-NK92 cells co-cultured with MCF-7 ICI-R#3 harboring shB7-H6 or the control shRNA of luciferase (shLuc). Results are presented as mean ± SD based on three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by t-test: **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001. F. IFN-γ production of NCR3-NK92 cells co-cultured with MCF-7 ICI-R#3 harboring shB7-H6 or shLuc. Statistical significance was determined by t-test. *, P < 0.05.