Figure 2.
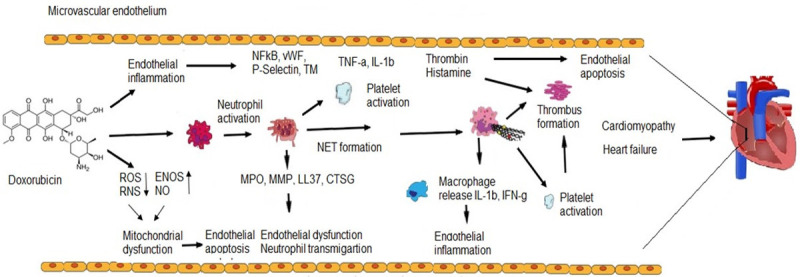
DOX-induced cardiomyocytes damage is preceded by vascular endothelial injury associated with neutrophil degranulation and NET formation. DOX induces ROS generation, inactivation of NO production, endothelial dysfunction and recruitment of neutrophils. Pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted by monocytes, lymphocytes and ECs activate neutrophil degranulation. Neutrophil granule proteins participate in the disruption of EC structure, leading to endothelial inflammation, neutrophil transmigration and apoptosis. NETs provide scaffold for platelet activation and deposition, thus promoting thrombosis formation.
