Fig. 2.
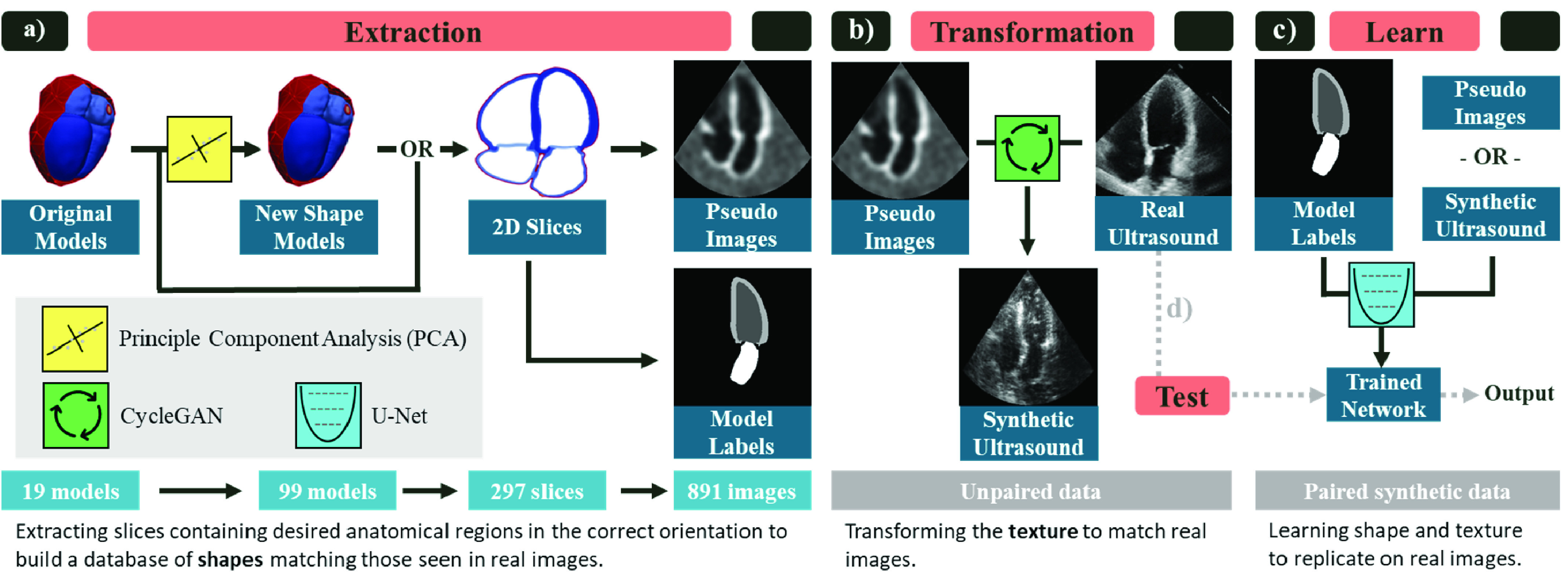
Overview of proposed pipeline implemented for echocardiography segmentation. a) Extraction: pseudo images and ground truth labels are built from the 3D anatomical models. First, a larger cohort of shapes is generated by building a statistical shape model from the original anatomies and sampling new 3D instances using principle component analysis (PCA). Next, 2D slices of the desired view (apical four chamber shown) are sampled. Finally, pseudo-ultrasound images and the corresponding labels are built. Each step expands the size of the dataset. b) Transformation: The pseudo images and a dataset of unlabeled real echo images are used to train a CycleGAN to transform the pseudo images into synthetic ultrasound images. c) Learn: The paired synthetic ultrasound images and model labels are used to train a U-Net segmentation network. d) Test: The network trained on synthetic images is tested on real images to evaluate the utility of the pipeline. The creation of new shape models as well as the transformation module are optional extensions. The slicing can be performed on the original models and the segmentation network can be trained using pseudo images instead. We evaluate the effectiveness of these components in Sec. IV.
