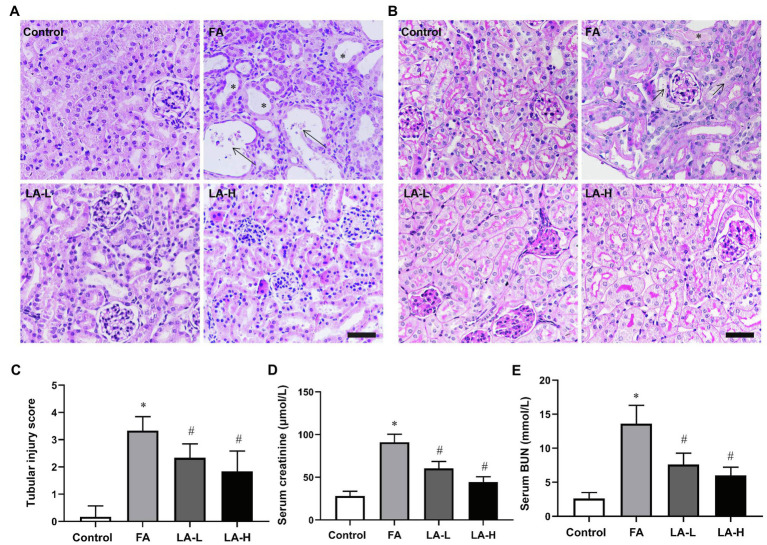
Figure 1.
The protective effects of lipoic acid (LA) supplementation on folic acid (FA)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). FA group mice are given an intraperitoneal injection of FA at 250mg/kg body weight once, without or with LA-L (50mg/kg body weight) or LA-H (100mg/kg body weight) supplementation. (A) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, showing the histological changes in FA-induced AKI and the LA-treated groups. Bar=50μm. Asterisks for dilated tubule; arrows for necrotic tubular epithelial cells. (B) Renal damage is assessed by Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining. Bar=50μm. Asterisks for tubular ectasia and arrows for tubules with cells in necrosis and cellular debris. (C) Renal tubular injury scores on the basis of H&E staining. The renal function is evaluated by (D) serum creatinine and (E) serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels. For the FA group vs. the control group, *indicates p<0.05, and **indicates p<0.01. For the LA-treated groups vs. the FA group, #indicates p<0.05, and ##indicates p<0.01.