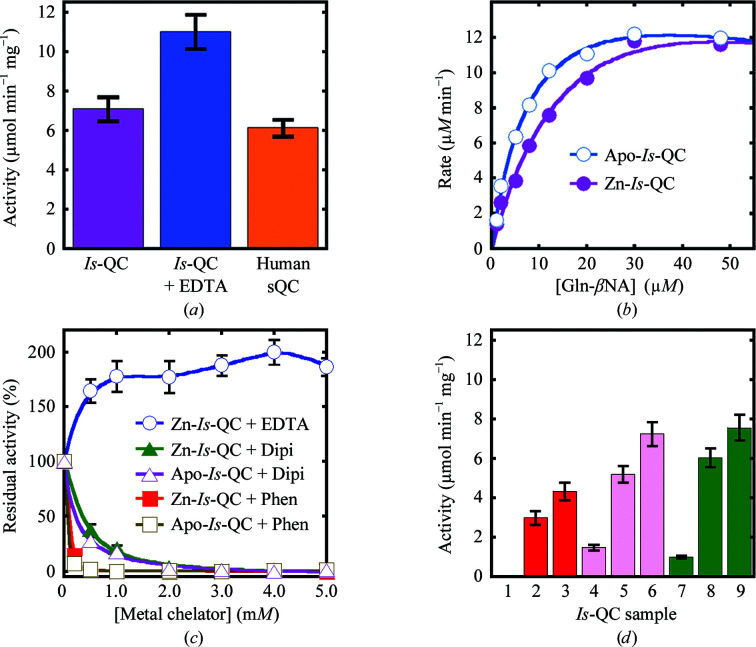
Figure 2.
Enzymatic activity of Is-QC and its modulation by metal-chelating agents. (a) Activities of Zn-Is-QC (purple) and apo-Is-QC (blue) and comparison with the activity of human sQC (orange). The activities ± SD were calculated from three independent experiments. (b) Enzyme-kinetic analysis of Zn-Is-QC and apo-Is-QC. The typical result of three experiments is presented. (c) Activities of Zn-Is-QC and apo-Is-QC in the presence of EDTA, dipicolinic acid (Dipi) or 1,10-phenanthroline (Phen). Before addition to the reaction mixture, the QC samples were pre-incubated with the metal-chelating agents at the indicated concentrations for 30 min. The results were calculated as residual activities ± SD from three independent experiments. (d) Restoration of Is-QC activity. Columns 1, 4 and 7: Zn-Is-QC was passed through a Sephacryl S-100 size-exclusion column in the presence of 5 and 1 mM 1,10-phenanthroline and 5 mM dipicolinic acid, respectively, and the QC activities of the resulting Is-QC samples were analyzed. Columns 2, 5 and 8: the Is-QC samples in columns 1, 4 and 7, respectively, were re-passed through a second Sephacryl S-100 column to remove the metal-chelating agents and the QC activities of the resulting samples were analyzed. Columns 3, 6 and 9: the Is-QC samples in columns 2, 5 and 8 were analyzed for QC activity in the presence of 1 mM EDTA. All enzymatic activity assays were performed at 25°C in 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0 using the fluorescent substrate Gln-βNA.