Figure 5.
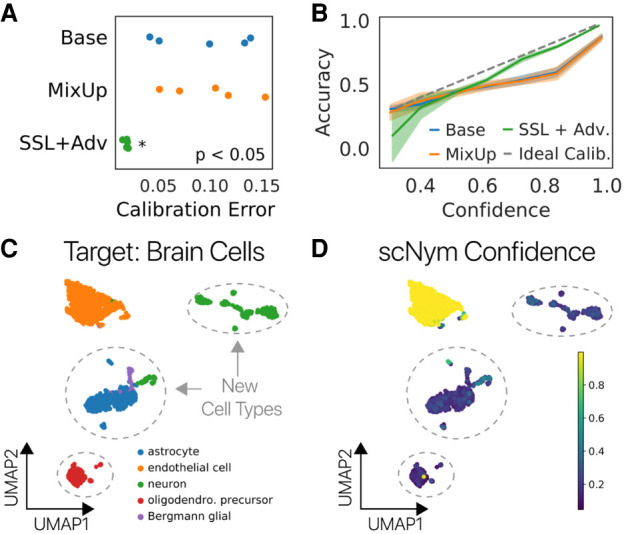
scNym confidence scores highlight unseen cell types. (A) scNym calibration error for models trained on the human PBMC cross-stimulation task. Semisupervised and adversarial training significantly reduced calibration error relative to models trained with only supervised methods (Base, MixUp). (B) Calibration curves capturing the relationship between model confidence and empirical accuracy for models in A. (C) scNym models were trained to transfer annotations from a mouse atlas without brain cell types to data from mouse brain tissue. We desire a model that provides low-confidence scores to the new cell types and high-confidence scores for endothelial cells seen in other tissues. (D) scNym confidence scores for target brain cells. New cell types receive low-confidence scores as desired (dashed outlines).
