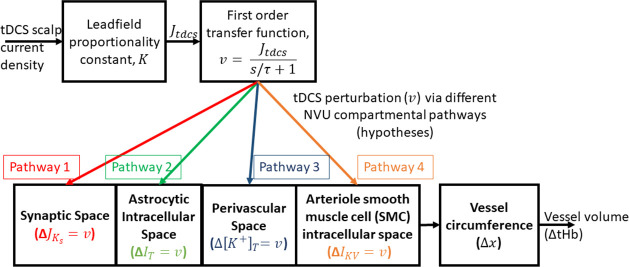
Fig 6. Schematic representation of the four pathways for tDCS current density effects (perturbation) on vessel volume function related to vessel circumference changes for hypothesis testing using experimental total hemoglobin (tHb) concentration changes (proportional to blood volume).
The four simulated pathways are, Pathway 1: tDCS current density (input pulse) via first-order transfer function modulate vessel volume response (output) by perturbing synaptic potassium (K+) released from active neurons (), Pathway 2: tDCS current density (input pulse) via first-order transfer function modulate vessel volume response (output) by perturbing the astrocytic transmembrane current (ΔIT), Pathway 3: tDCS current density (input pulse) via first-order transfer function modulate vessel volume response (output) by perturbing perivascular potassium (K+) concentration (Δ[K+]T), and Pathway 4: tDCS current density (input pulse) via first-order transfer function modulate vessel volume response (output) by perturbing voltage-gated ion channel current (ΔIKV) on the smooth muscle cell (SMC).