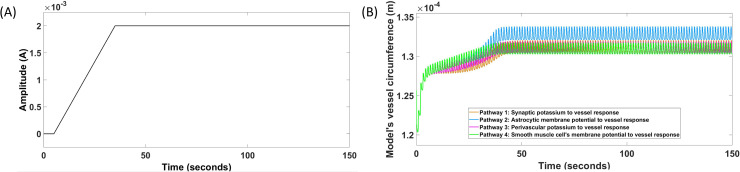
Fig 8.
Physiologically detailed neurovascular coupling model showing the input HD-tDCS current (A) and the output vessel circumference response for the four simulated pathways for duration 0-150sec (B). Pathway 1: tDCS current density perturbing vessel circumference through synaptic potassium pathway, Pathway 2: tDCS current density perturbing vessel circumference through the astrocytic pathway, Pathway 3: tDCS current density perturbing vessel circumference through perivascular potassium pathway, and Pathway 4: tDCS current density perturbing vessel circumference through smooth muscle cell voltage-gated ion current channels pathway. Shown in (B), all the tDCS perturbation pathways has an initial transient response, and then generated steady-state vessel oscillations.