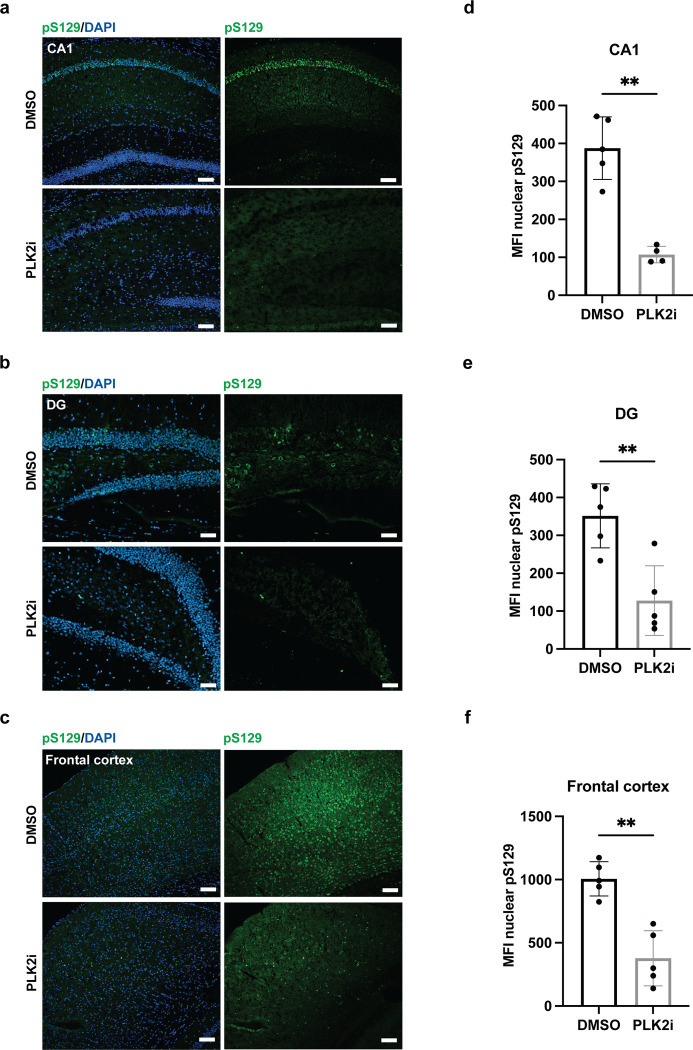
Fig 5. PLK2i treatment for 48 hours before sacrifice reduces nuclear pS129-staining in PFF-injected M83 mice.
a-c) Representative images from the CA1 region (a) and the DG (b) of hippocampus, and the frontal cortex (c) of 15-month-old M83 mice– 3 months following PFF injection in the hindlimbs–stained with pS129 (D1R1R) and DAPI, showing particularly strong pS129-staining at pyramidal neurons of the CA1 region. 48-hour PLK2i treatment by oral gavage (2 x 100 mg/kg/day) significantly reduces nuclear pS129-staining in all regions, although some PLK2i resistant S129-phosphorylation is apparent in the frontal cortex. Scale bars = 50 μm. d-f) Quantification of the mean fluorescence intensity of nuclear pS129 in CA1 with 73.3% reduction following PLK2i treatment, p-value = 0.0010 (d), in DG with 63.7% reduction, p-value = 0.0040 (e), and in the frontal cortex with 62.5% reduction, p-value = 0.0011 (f). All comparisons were made using an unpaired Welch’s T test. Bars represent the mean ± SD, n = 5 mice in each group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.