Figure 4.
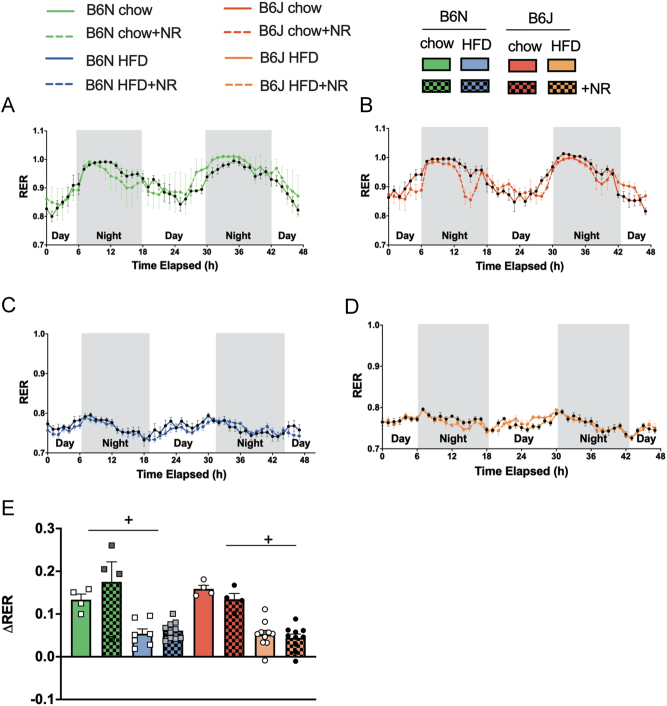
Substrate usage is not altered by NR supplementation. The respiratory exchange ratio (RER) as a measure for substrate usage was determined by indirect calorimetry in metabolic cages. The time course of RER measurement is shown in (A) chow-fed B6N, (B) chow-fed B6J, (C) HFD-fed B6N, and (D) HFD-fed B6J mice. ΔRER as a measure for metabolic flexibility was calculated by subtracting the five lowest values during the day from the five highest values during the night and is shown in (E). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m., n = 4 for chow, n = 7 for B6N HFD, n = 10 for B6N HFD+NR, B6J HFD, and HFD+NR. Tests for statistical significance were done using ordinary two-way ANOVA with diet and mouse strain as factors followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. Data for NR vs no NR supplementation were analyzed together since no significant differences were found for NR vs no NR. +P < 0.05 for HFD vs chow.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a