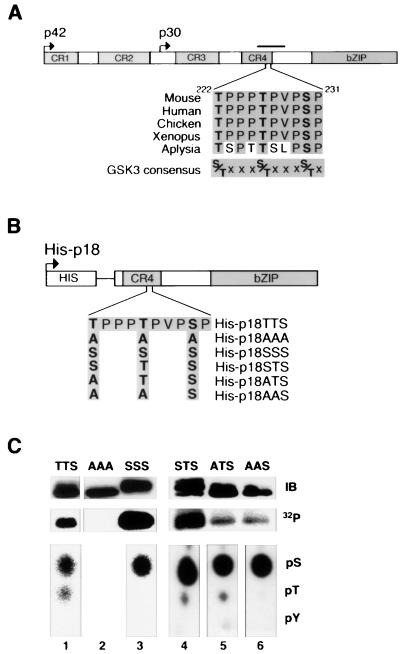
FIG. 1.
Identification of phosphorylation sites in C/EBPα. (A) A schematic diagram of C/EBPα. Regions that are highly conserved across species (conserved regions 1 to 4 and bZIP domain) are shaded. Bent arrows denote translational start sites for two predominant C/EBPα species (p42C/EBPα and p30C/EBPα). A phosphopeptide identified in three independent labeling experiments is indicated by the solid bar. Amino acids within a region of this phosphopeptide are shown for mouse, human, chicken, Xenopus, and Aplysia proteins. The consensus sequence for GSK3 is given. (B) Schematic representation of the His-tagged C/EBPα fusion proteins used in subsequent labeling experiments. The C/EBPα amino acid sequence from T222 to P231 is given, and the C/EBPα mutants in which T222, T226, and S230 were mutated to either alanines or serines are illustrated. (C) His-p18TTS (lane 1), His-p18AAA (lane 2), His-p18SSS (lane 3), His-p18STS (lane 4), His-p18ATS (lane 5), and His-p18AAS (lane 6) were expressed in 293T cells, labeled with 32P in vivo, purified, and separated by SDS-PAGE. These samples were subjected to immunoblot analysis for C/EBPα (top panel; IB) and autoradiography (middle panel; 32P). Phosphoamino acid analysis was performed with the remainder of the His-tagged C/EBPα mutants (bottom panels). The positions of phosphoserine (pS), phosphothreonine (pT), and phosphotyrosine (pY) are indicated. His-p18AAA contained no detectable 32P.