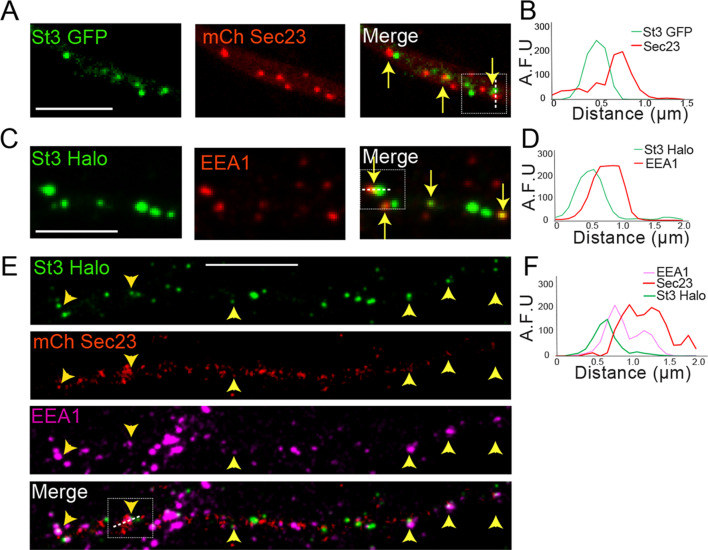
Figure 4. Dendritic Golgi satellites localize near endoplasmic reticulum exit sites (ERESs) and endosomes.
(A) Golgi satellites (St3-GFP) frequently pair with ERESs (mChSec 23) in dendrites. Primary cortical cultures were transfected with St3-GFP, mCh-Sec23, and HA-tagged α4β2R subunits. Neurons were treated with nicotine for 17 hr and fixed. Dendrites were imaged for Golgi satellites (St3-GFP, green) and ERESs (mChSec 23, red). Closely aligned Golgi satellites and ERESs are marked by yellow arrows. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) An example of the close association between Golgi satellites (green) and ERESs (red). Signal intensity of the Golgi satellite and ERESs measured in arbitrary fluorescent units (AFU) in a line scan through the pair in the boxed area. (C) Golgi satellites (St3-GFP) frequently pair with early endosomes (EEA1 staining) in dendrites. Neurons were transfected with St3-GFP and after nicotine treatment, fixed and stained with antibodies to EEA1 before imaging as in A. Golgi satellites closely aligned with early endosomes are marked by yellow arrows. Scale bar, 5 µm. (D) An example of the close association between Golgi satellites (green) and early endosomes (red). Signal intensity of the two compartments was measured and displayed as in A. (E) Golgi satellites (St3-Halo) frequently form triads with ERESs (mChSec 23) and early endosomes (EEA1 staining) in dendrites. Neurons were transfected with St3-GFP, mCh-Sec23, and treated with nicotine for 17 hr before fixation and antibody labeling for EEA1 and imaging. Golgi puncta (green) closely aligned with ERESs (red) and early endosomes (mauve) are marked by yellow arrow heads. Scale bar, 10 µm. (F) An example of the close association between Golgi satellites (green), ERESs (red), and early endosomes (mauve). Signal intensity for markers of the three organelles was measured and displayed as in A and C.