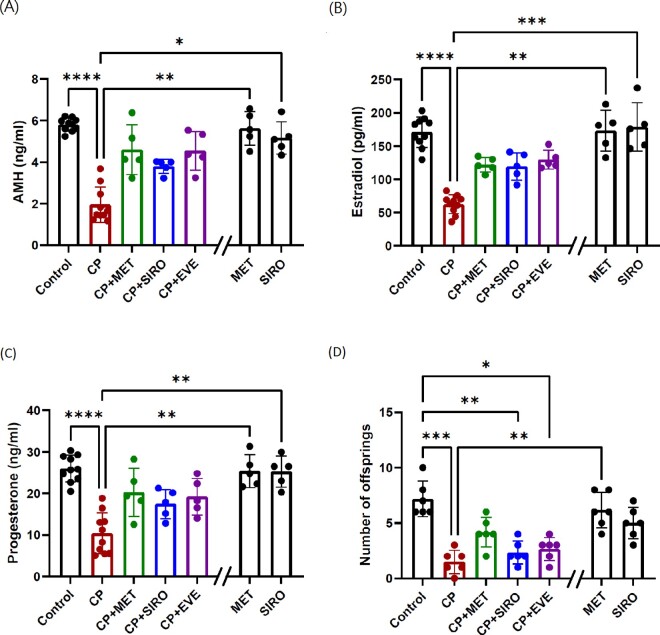
Figure 2.
The serum hormone concentration and the number of offspring in each group. C57BL/6 mice were treated with CP-alone, metformin (MET)-alone, sirolimus (SIRO)-alone, or CP in combination with MET, SIRO or everolimus (EVE). After 4 weeks of treatment, the mice were sacrificed and serum was collected for hormonal determination. (A) The serum levels of anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) were significantly decreased in the CP-alone group (compared with control group: P < 0.0001). Although the AMH levels increased in CP + MET, CP + SIRO and CP + EVE group, the data did not reach statistical significance probably due to limited case number. (B) The serum levels of estradiol were significantly decreased in the CP-alone group (P < 0.0001), and tended to increase in CP + MET group, CP + SIRO group and CP + EVE group. (C) The serum levels of progesterone were significantly decreased in the CP-alone group (P < 0.0001) and tended to increase in CP + MET group and CP + EVE group. (D) A breeding test was conducted 1 week after the 4-week treatment. Only one round of timed mating was conducted per female mouse and the outcome of the first pregnancy in each mouse was evaluated. The number of the offspring was significantly decreased in the CP-alone group (P < 0.0001) and tended to increase in the CP + MET group. In (A)–(C), n = 10 mice in the control and CP-alone group, while n = 5 mice in the other groups. In (D), n = 6 mice per group. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analyses were performed by nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's post-hoc for multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Note: The double slash mark on the X axis separated the MET-alone and SIRO-alone group from other groups because these two control groups were run in a separate experiment.