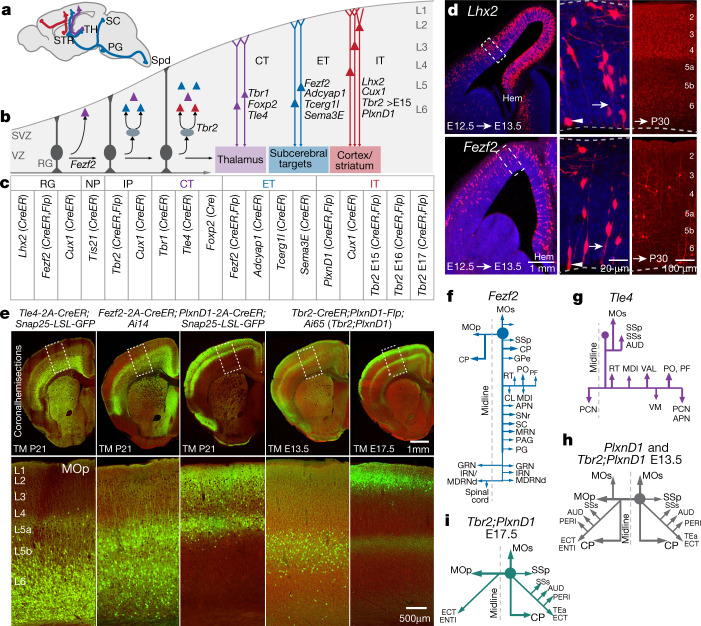
Fig. 5. Genetic tools for targeting cortical glutamatergic projection neuron types.
a, Major PyN projection classes mediating IT (red) and cortical output channels (ET, blue; CT, purple). PG, pontine grey; Spd, spinal cord. b, Developmental trajectory from progenitors to mature PyNs. Genes specify lineage and projection types. VZ, ventricular zone; SVZ, subventricular zone. c, New gene knockin driver mouse lines targeting RG, neurogenic precursor (NP), IP and broad projection types. d, Pulse-chase of E12.5 Lhx2-2A-CreER;Ai14 (Lhx2) (top row) and Fezf2-2A-CreER;Ai14 (Fezf2) (bottom row) embryos for 24 hours densely labelled RGs throughout dorsal neuroepithelium (left). Middle, boxed areas shown left, magnified, showing RGLhx2+ and RGFezf2+. Long pulse-chase (right) of E12.5 RGs generates PyNs across layers at postnatal day (P)30. Arrows show endfeet and arrowheads show dividing soma. Hem, cortical hemisphere. e, Driver–reporter recombination patterns (reporter, pseudo-coloured green; background, red) from five PyN subpopulations defined by Tle4, Fezf2, PlxnD1 and Tbr2;PlxnD1 with tamoxifen (TM) induction times. Combinatorial definition of PyNPlxnD1 subtypes by lineage, birth time and anatomical location achieved by Tbr2;PlxnD1 intersection: tamoxifen at E13.5 and at E17.5 labelled different Tbr2-expressing IP-derived PyNPlxnD1 cohorts. Boxed areas in MOp (top row) are shown in the bottom row. f–i, Main PyN subpopulation projection targets from MOp. Drivers were crossed with mouse reporter lines, Rosa26-CAG-LSL-Flp (Cre-dependent) or Rosa26-CAG-dual-(LSL-FSF)-tTA (Cre-AND-Flp-dependent), and tamoxifen induction was performed to convert transient CreER to constitutive reporter expression for anterograde tracing with Flp- or tTA-dependent AAV vector (AAV8-CAG-fDIO-TVA-EGFP or AAV-TRE-3g-TVA-EGFP). Filled circle shows MOp injection site. For full names of projection target acronyms, see refs. 34,47. APN, anterior pretectal nucleus; AUD, auditory cortex; CL, central lateral nucleus; ENTI, entorhinal area, lateral part; GPe, globus pallidus, external segment; GRN, gigantocellular reticular nucleus; IRN, intermediate reticular nucleus; MDl, mediodorsal nucleus, lateral part; MDRNd, medullary reticular nucleus, dorsal part; MRN, midbrain reticular nucleus; PAG, periaqueductal grey; PCN, paracentral nucleus; PF, parafascicular nucleus; RT, reticular nucleus; SNr, substantia nigra, reticular part; SSs, supplemental somatosensory cortex.