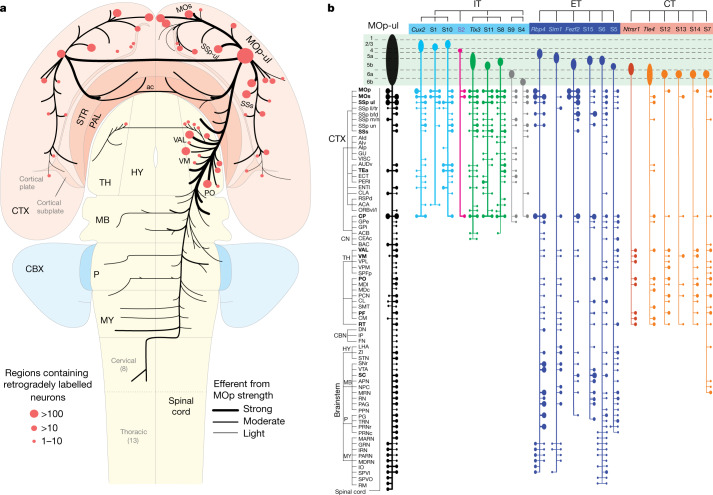
Fig. 6. Global wiring diagram and anatomical characterization of MOp-ul neuron types.
a, Flat map representation of the MOp-ul input–output wiring diagram. Black lines and red dots indicate axonal projections (outputs) and retrograde labelling sources (inputs), respectively, with line thickness and dot sizes representing relative connection strengths. Most MOp-ul projection targets in the cortex and TH also contain input sources, suggesting bi-directional connections. Numbers in parentheses indicate numbers of cervical or thoracic segments in spinal cord. b, Projection patterns arising from excitatory cell subclasses, IT, ET and CT, with corresponding Cre line assignment and somatic laminar location, compared with the overall projection pattern from the MOp-ul region (left, black). Along each vertical output pathway, horizontal bars on the right and left sides represent ipsilateral and contralateral collaterals, respectively, with dot sizes indicating the strength of axonal termination in different targets. For full names of projection target acronyms, see refs. 34,44. ac, anterior commissure; ACB, nucleus accumbens; AId, v, p, agranular insular cortex, dorsal, ventral, posterior part; AUDv, ventral auditory cortex; BAC, bed nucleus of the anterior commissure; CBN, cerebellar nuclei; CBX, cerebellar cortex; CEAc, central amygdalar nucleus, capsular part; CM, central medial nucleus; CN, cerebral nuclei; CTX, cerebral cortex; DN, dentate nucleus; FN, fastigial nucleus; GPi, globus pallidus, internal segment; GU, gustatory cortex; HY, hypothalamus; IO, inferior olivary complex; IP, interposed nucleus; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; MARN, magnocellular reticular nucleus; MB, midbrain; MDc, mediodorsal nucleus, central part; MDRN, medullary reticular nucleus; NPC, nucleus of the posterior commissure; ORBvl, l, orbital cortex, ventrolateral, lateral part; P, pons; PAL, pallidum; PARN, parvicellular reticular nucleus; PPN, pedunculopontine nucleus; PRNr, pontine reticular nucleus; PRNc, pontine reticular nucleus, caudal part; RM, nucleus raphe magnus; RN, red nucleus; RSPd, retrosplenial cortex, dorsal part; SMT, submedial nucleus; SPFp, subparafascicular nucleus, parvicellular part; SPVI, spinal nucleus of the trigeminal, interpolar part; SPVO, spinal nucleus of the trigeminal, oral part; SSp-ul, -ll, -tr, -bfd, -m, -n, -un, primary somatosensory cortex upper limb, lower limb, trunk, barrel field, mouth, nose, unassigned; STN, subthalamic nucleus; TRN, tegmental reticular nucleus; VISC, visceral cortex; VPL, ventral posterolateral nucleus; VPM, ventral posteromedial nucleus; ZI, zona incerta.