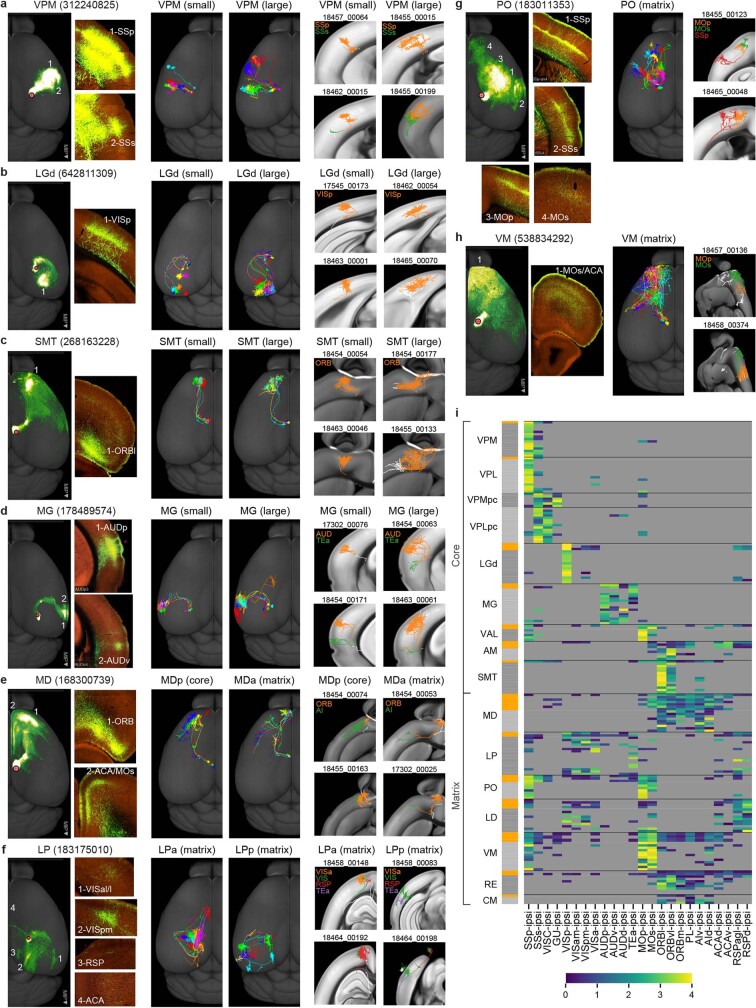
Extended Data Fig. 12. Long-range projection patterns of individual thalamic neurons in comparison with mesoscale population-level projections.
a–h, Axonal morphologies and projections of reconstructed single neurons compared with population projection patterns for thalamic nuclei VPM (a), LGd (b), SMT (c), MG (d), MD (e), LP (f), PO (g) and VM (h). For each nucleus: left panels, representative mesoscale experiments shown in a maximum projection whole-brain top-down view and individual higher-power images showing axon termination patterns in major target regions; middle panels, representative single neurons shown together in a whole-brain top-down view; right panels, each representative neuron is shown in a chosen plane to best capture the perpendicular (to pial surface) orientation of the main axon arbor with superimposed maximum projection view of the neuron’s axon arbors. The chosen plane can be coronal (for a, b, d), horizontal (for c, e), sagittal (for h) or tilted (for f, g), based on the main cortical target region. Different cortical target regions are indicated by different colors. Small, small axon arbors. Large, large axon arbors. MDa and MDp, or LPa and LPp are the anterior and posterior parts of MD or LP respectively. i, Projection matrix showing comparison of thalamocortical projection patterns between mesoscale experiments and single neurons as well as among individual neurons, for each listed thalamic nucleus. Each row is a mesoscale experiment (labeled in orange in the left side bar) or a single cell (labeled in grey in the left side bar). Heatmap colors represent projection strengths, defined as ln(NPV × 100 + 1) for mesoscale experiments and ln(axon length) for single cells. Target regions are defined using thresholds of ln(NPV × 100 + 1) > 0.2 for mesoscale experiments and axon length > 1 mm for single cells. Regions below the thresholds are shown in grey. Overall, core-type thalamocortical neurons usually have one major axon arbor targeting L4 of the primary sensory or motor cortex of the corresponding modality, i.e., VPM and VPL projecting to SSp, VPMpc to gustatory areas (GU), VPLpc to visceral area (VISC), LGd to primary visual area (VISp), MG to auditory areas (AUD), and VAL to MOp. Reconstructed neurons from AM, SMT and posterior MD also send a single major axon arbor to various parts of orbital cortex (ORB), with a similar mid-layer termination pattern, suggesting these neurons also belong to the “core” projection type. A small fraction of the core-type neurons (5.43% for VPM, 4.05% for VPL, 15.6% for MG, but 0% for LGd) have more than one axon arbor targeting different cortical areas. In the case of these cells in VPM and VPL, usually they have a larger main arbor targeting SSp, and a smaller secondary arbor targeting SSs (a). MG neurons with two or more cortical targets are mostly of the large-arbor type (d). These multi-target MG neurons are more like the matrix-type neurons, showing stronger projections to L1 and L5, located in the associational parts of MG (e.g., MGm) medial to the core relay auditory nucleus, MGd and MGv. Single neurons are assigned to either small-arbor or large-arbor type (Extended Data Fig. 13). Large-arbor neurons account for 32.0% of the total reconstructions from VPM, 31.9% from VPL, 38.9% from LGd and 36.0% from MG. Neurons in SMT are also separable into small- and large-arbor types, whereas the current set of AM neurons all have small arbors and the posterior MD neurons all have large arbors. Matrix-type thalamocortical neurons exhibit a diverse range of projection and morphological patterns. For example, LP neurons preferentially project to two or more higher visual cortical areas. They do not directly project into VISp, 6 out of 16 reconstructed LP neurons has short axon fibers in VISp (average ~2 mm in VISp, substantially below the average of LGd neurons, ~26 mm). LP neurons can be roughly divided into an anterior and a posterior group, consistent with previous functional studies71. Posterior LP neurons mainly project to lateral and posterior higher visual areas, whereas anterior LP neurons mainly project to medial and anterior higher visual areas with some extending an axon projection into anterior cingulate cortex (ACA) (f). PO neurons project to both SSp and MOp/MOs. Their axon arbors in these target regions terminate broadly across layers with an apparent preference in L4 and lower L2/3, with 4 out of 7 sending rich axon arbors (> 1 mm) to L1 (g). Neurons in anterior MD appear very different from those in posterior MD and are more similar to those in neighboring nuclei such as IAD and CM. They have multiple axon arbors that target multiple medial and lateral prefrontal cortical areas including prelimbic cortex (PL), ORB and agranular insular cortex (AI) (e). VM neurons have multiple axon arbors, heavily targeting MOp and/or MOs with additional branches targeting various somatosensory areas (h).