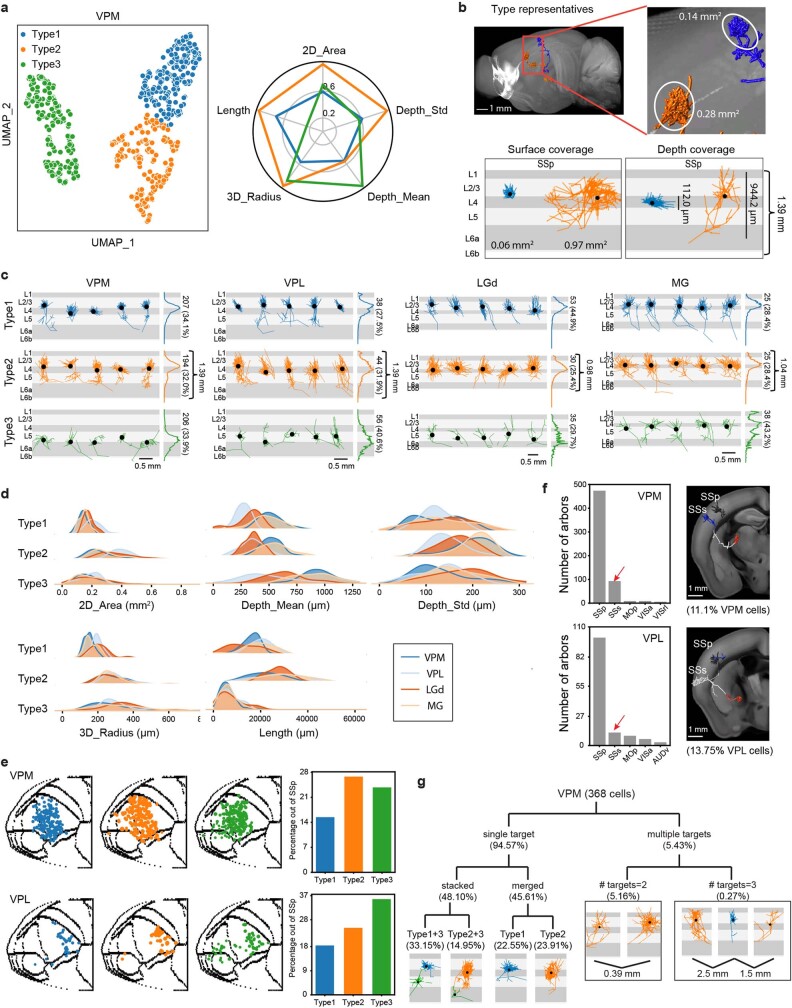
Extended Data Fig. 13. Thalamocortical axon arbor analysis.
Clustering of 944 cortical axon arbors from 586 neurons from VPM, VPL, LGd and MG reveal three types of arbors. Two major types of axon arbors target cortical layer 4 (spanning L4 and lower L2/3); a smaller 'type 1' arbor and a larger 'type 2' arbor (cortical area > 0.3 mm2). The 'type 3' arbor terminate in cortical L6; this type is most often a minor collateral originating from the type 1 or type 2 arbor, so we did not use it to classify neurons. a, Clustering result indicates three types of cortical axon arbors in VPM neurons. Left, UMAP representation of VPM axon arbors. Right, polar plot of main features, values as normalized cluster averages. b, Representative (upper) and extreme (lower) examples of VPM cortical arbors. c, Examples grouped by thalamic nuclei and arbor types. In each sub-panel, vertical views are shown for 5 representative arbors, with branch length distribution for all neurons of the same cluster on the right side. Arbor number and percentage of the group are shown on the right side. d, Distribution of features grouped by thalamic nuclei and arbor types. e, Arbor locations of VPM and VPL neurons in 2D cortical map grouped by arbor types. Each dot represents the center of an arbor. Somas with small and large arbors are spatially intermingled in each nucleus. Right panels show percentage of arbors outside of the primary target of VPM or VPL neurons. f, (Left) Counts of VPM or VPL arbors in cortical regions. (Right) Examples of neurons with double arbors, one in SSp and the other in SSs. g, Variation of VPM neurons by arbor composition. ‘Single target’ neurons are described as ‘stacked’ or ‘merged’ by bi-layer or single-layer distribution. The stacked and merged groups can be further separated by arbor types. The ‘multiple targets’ group is divided by number of targets.