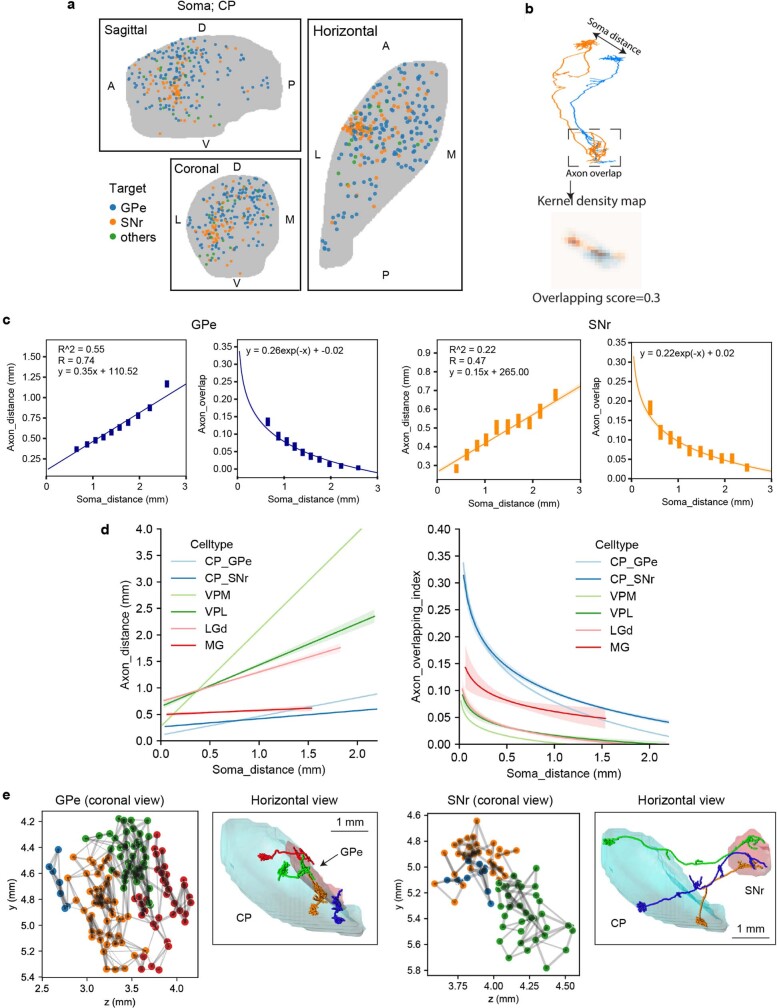
Extended Data Fig. 14. Striatal neuron morphologies.
a, Sagittal, coronal and horizontal views of soma distribution of CP neurons. Axes: D-V, dorsal to ventral; A-P, anterior to posterior; M-L, medial to lateral. We reconstructed 311 neurons in the dorsal striatum (CP) from 4 Cre driver lines: Tnnt1, Plxnd1, Vipr2 and Pvalb (Supplementary Table 2). These neurons can be divided into 3 groups, largely intermingled with each other, based on their projection targets: those with main axon projections terminating in GPe (n = 180), SNr (n = 100) or within striatum itself (others, n = 31). b, Overlapping score of axons is calculated by estimating the kernel density map of individual axon arbors and the density-weighted average of overlapping areas for each arbor pair. c, Regression of distance between arbor centers (left panels) or overlapping score (right panels) in target regions (GPe or SNr) by soma distance. Linear and negative exponential models are used for distance and overlapping score, respectively. Vertical bars represent 95% confidence intervals of regression. d, Comparison of arbor convergence across cell types. Regression curves are generated by the same approach as in c. Colors represent cell types. Center lines represent regression curves between soma distance and axon center distance (left panel), or soma distance and axon overlapping score (right panel). Light-shaded bands represent 95% confidence intervals. e, Clustering of axon overlapping by Louvain algorithm. Coronal views show axon arbor locations colored by clusters. Width of grey lines represents overlapping scores between arbor pairs. Horizontal views show example single neurons to illustrate topography of CP neuron projections. Cells are colored by cluster identities. In addition, the GPe-projecting type also has more elaborate axon arborization near the soma. Sholl analysis shows that the number of local crossings (< 1 mm to soma) of the GPe-projecting type is 2.9 times that of the SNr-projecting type.