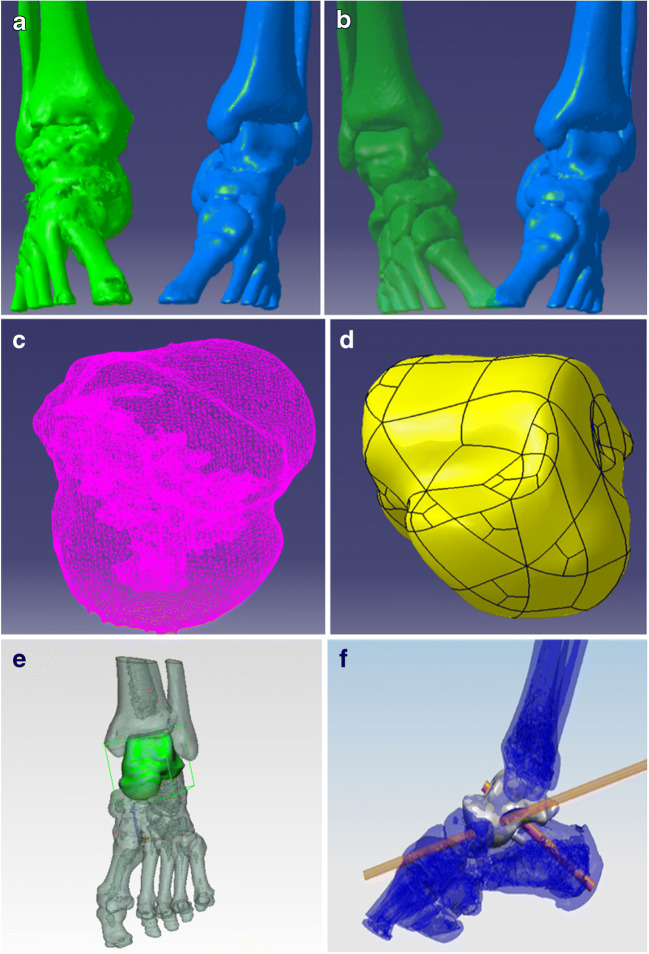
Fig. 1.
Individualized 3D modeling of talar prosthesis. a The data of the affected talus were acquired from the right foot, and the intact data were obtained from the intact foot. b The raw data for surgical reconstruction with the individualized talus were acquired by symmetrization and registration. C.Raw data for talar modeling were obtained with reverse repair technology. d The 3D talar prosthetic model was simulated. High-precision polishing and screw placement were included in the design of the prosthetic tibiotalar articular facet. e Determination of the locating column of the talar prosthesis. f The cannulated screw channel for fixation of the talonavicular and subtalar joints was stimulated