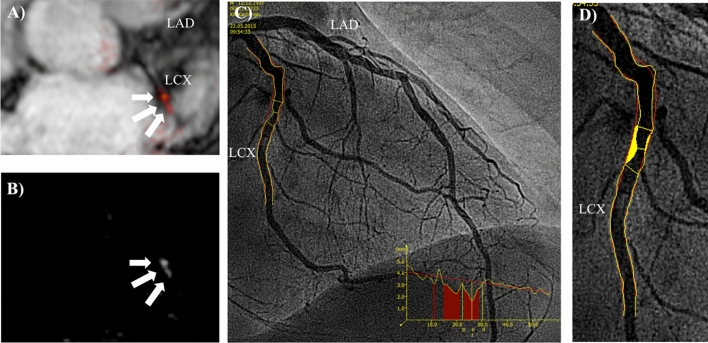
Fig. 1.
Representative images following the administration of an albumin-binding MR probe for the assessment of endothelial permeability and damage at sites of significant stenosis. To highlight the anatomical relationship between the uptake of the albumin-binding-MR probe (b) and morphology from the MR angiography, images were fused in a way comparable to positron emission tomography/computed tomography (a). Subsequent Invasive catheterization demonstrated a stenosis in the left circumflex artery (LCX) (c). The assessment using quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) revealed a stenosis of 73% (d). This sample case illustrates that CMR in combination with an albumin-binding probe is able to clearly identify coronary artery stenosis greater than 70%. Signal enhancement following application of gadofosveset-trisodium is known to be a surrogate for endothelial permeability and damage, which may be increased in severe stenosis